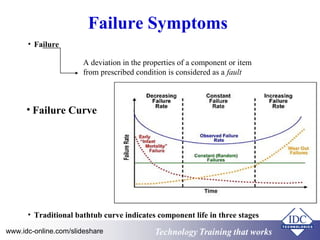
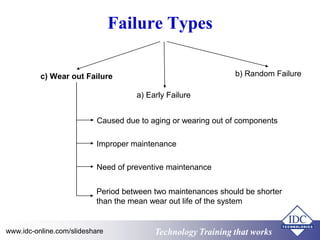
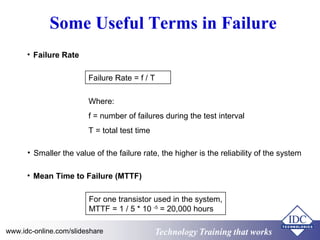
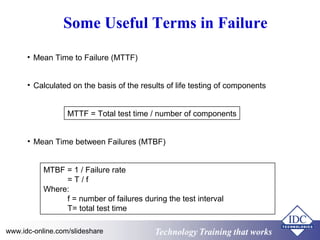
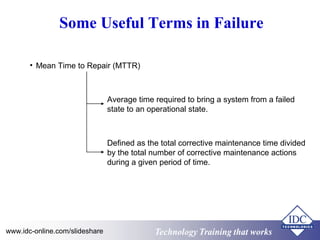
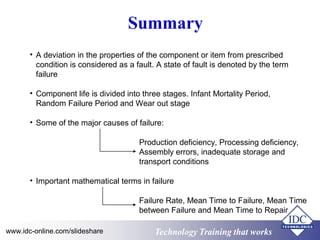
This document discusses failure analysis of electronic circuits. It defines failure and describes the traditional bathtub curve which indicates three stages of component life: infant mortality period, random failure period, and wear out stage. The document outlines objectives, failure symptoms, causes including design deficiencies and production deficiencies. It also defines failure types such as early failure, random failure, and wear out failure. Finally, it discusses useful terms for failure analysis such as failure rate, mean time to failure, mean time between failures, and mean time to repair.