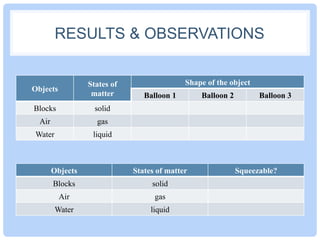
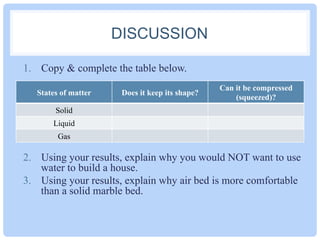
This document outlines an experiment to investigate the properties of solids, liquids, and gases. The experiment involves using balloons and a syringe to observe how these three states of matter behave in terms of shape and compressibility. In the experiment, blocks represent solids, air represents gases, and water represents liquids. The results show that solids maintain their shape in balloons and cannot be compressed in a syringe, while gases take the shape of their container and can be compressed, and liquids take the shape of their container but cannot be compressed.