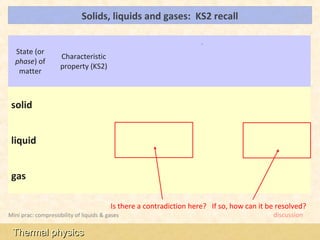
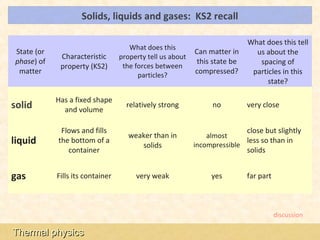
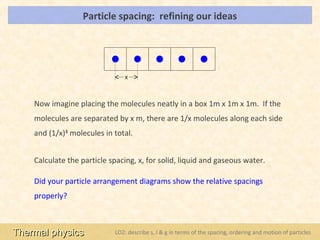
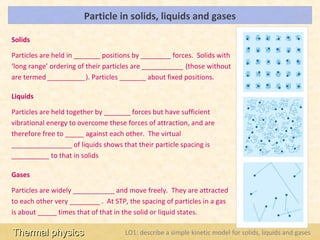
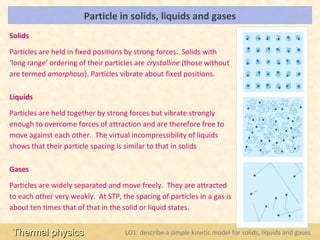
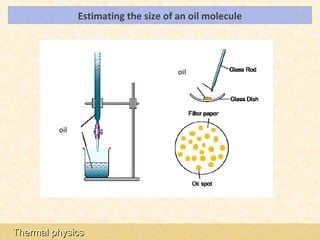
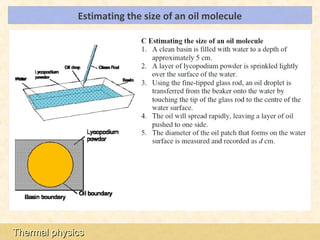
This document provides an overview of a lesson on solids, liquids and gases from an A-Level Physics unit on the Newtonian world. The lesson objectives are to describe a simple kinetic model of solids, liquids and gases, and describe the states in terms of particle spacing, ordering and motion. Key points covered include the kinetic theory of matter, particle arrangements in the different states, evidence for ordering in solids, calculating particle spacing, and describing the properties of particles in solids, liquids and gases.