This document provides an overview of functional groups in organic chemistry. It defines functional groups as atoms or groups of atoms that confer characteristic reactivity to molecules. The key points made are:
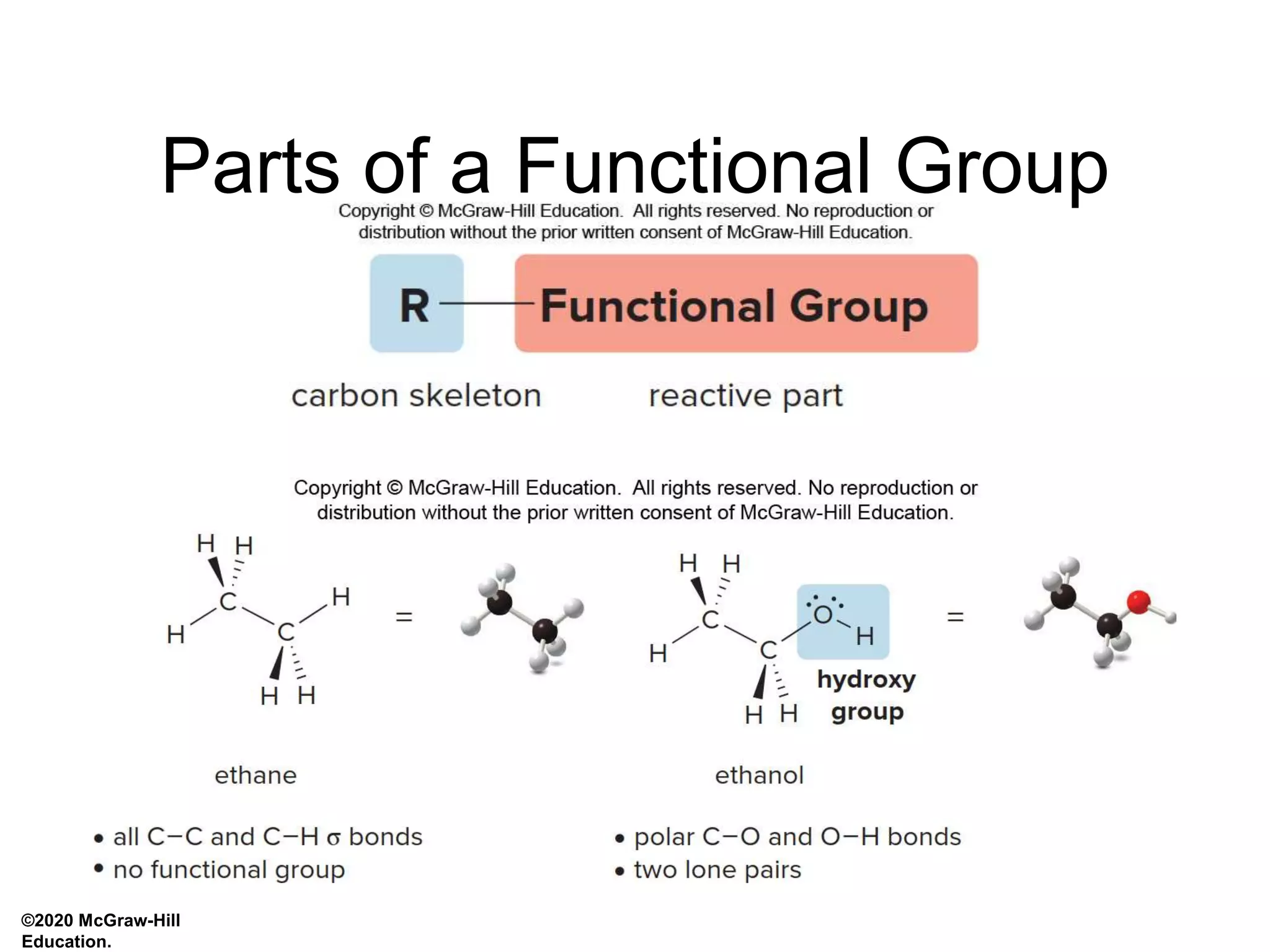
- Functional groups determine a molecule's geometry, physical properties, and reactivity. They distinguish one organic compound from another.
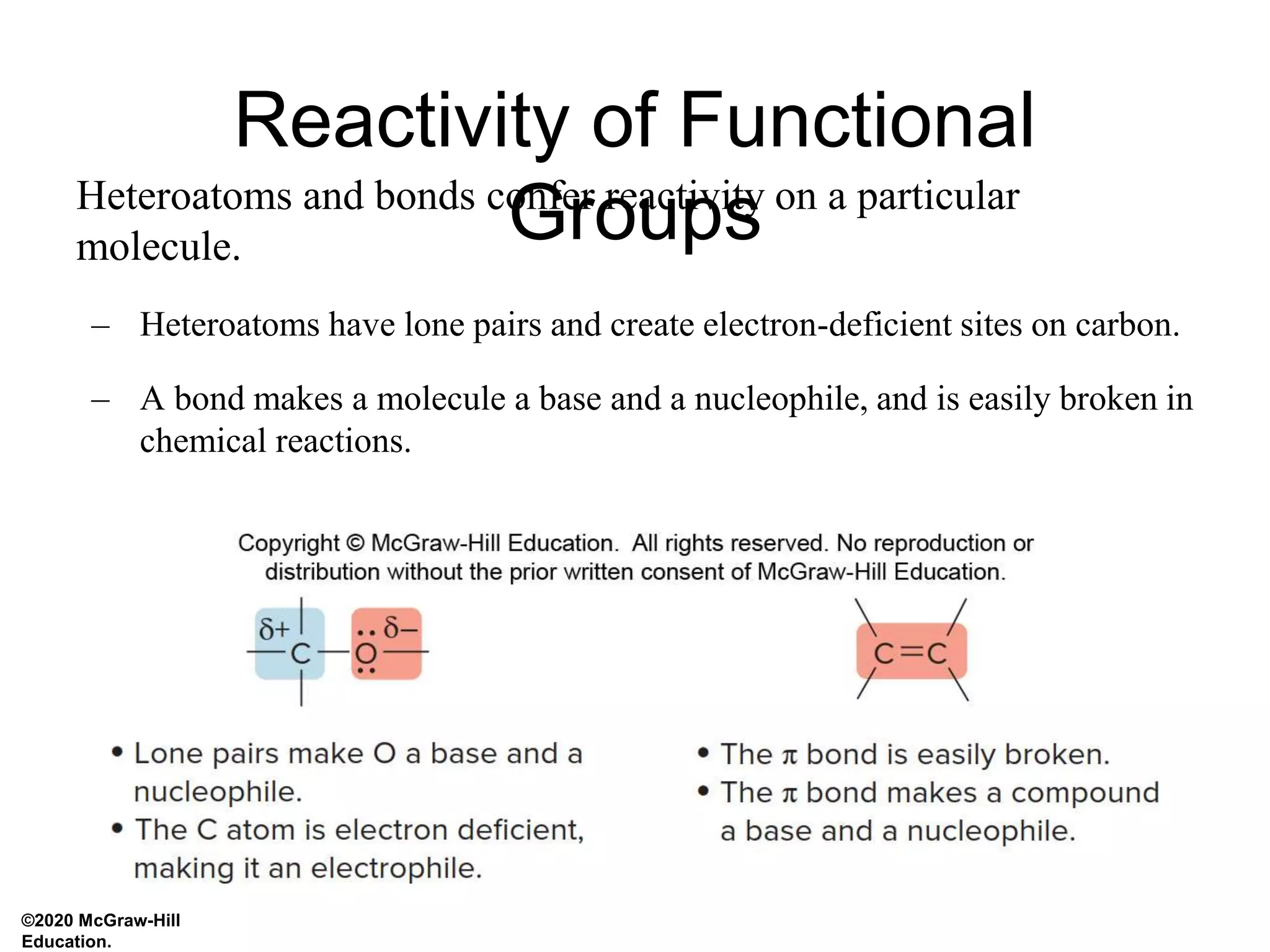
- Heteroatoms and pi bonds create electrophilic and nucleophilic sites that determine a molecule's reactivity. Electron-rich nucleophiles react with electron-deficient electrophiles.
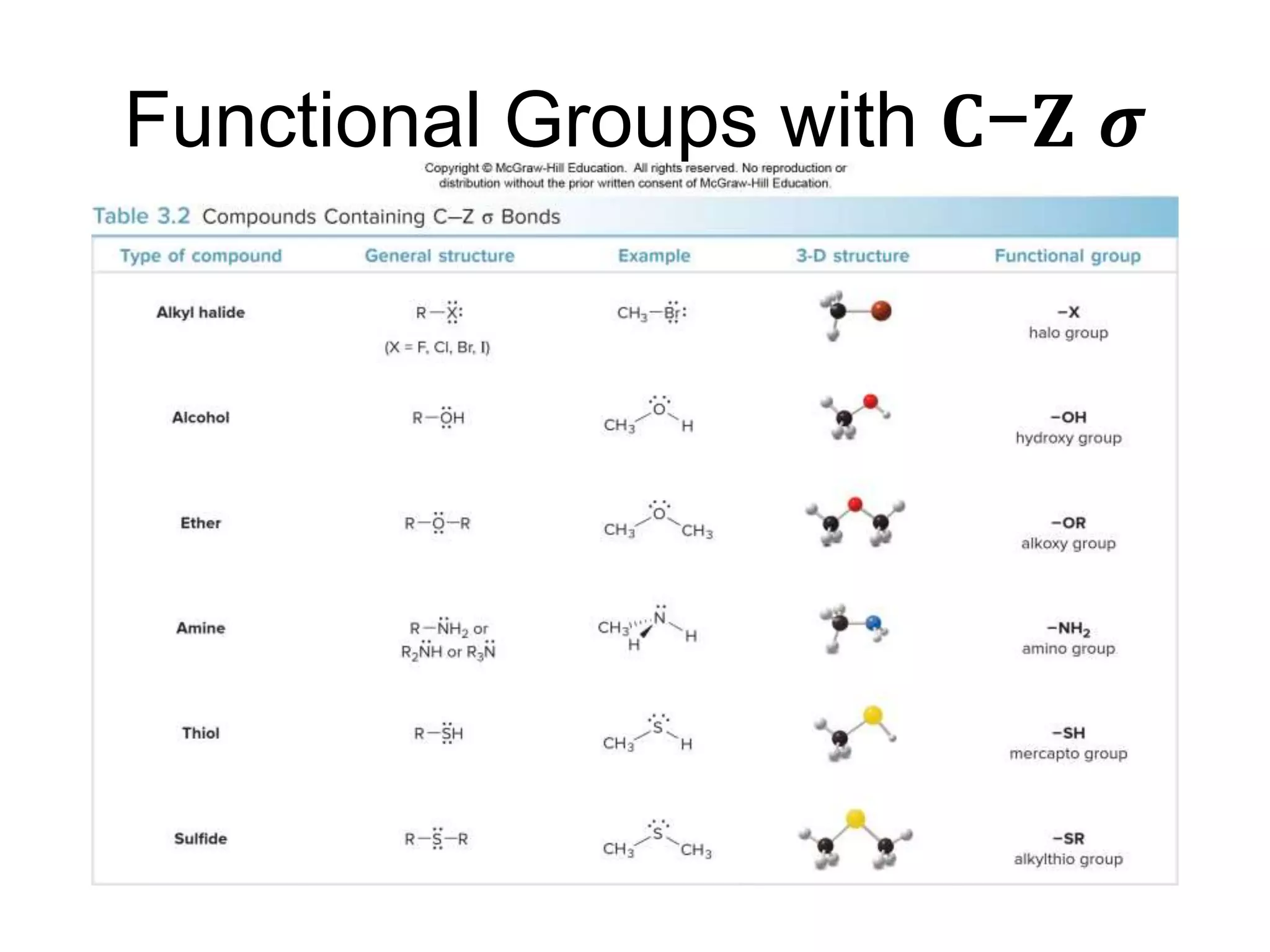
- Examples of important functional groups are given, like hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, and phosphate groups. Biomolecules often contain several different functional groups.