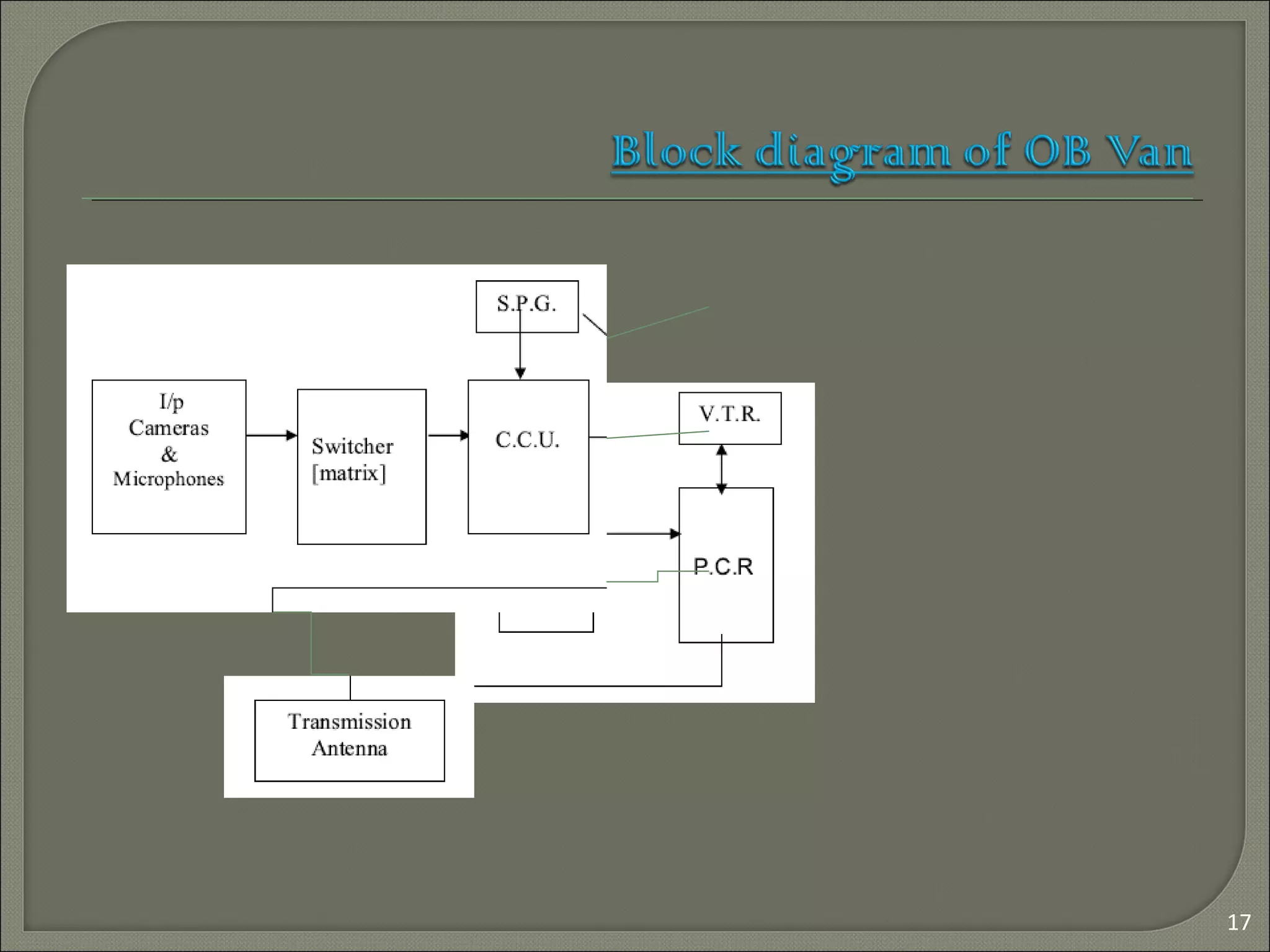
This document provides an overview of electronic media and television broadcasting in India. It discusses the history of broadcasting starting in 1923 with All India Radio and the first television station being established in 1959. It describes the key components of a television studio including cameras, lighting, mixers, and support equipment. Vision mixers are explained as the devices used to switch between video sources and add effects. Earth stations are described as important for satellite communication and broadcasting, sending signals to satellites for distribution. Outside broadcasting uses vans equipped for mobile TV production and transmission using microwave links or digital satellite news gathering systems.