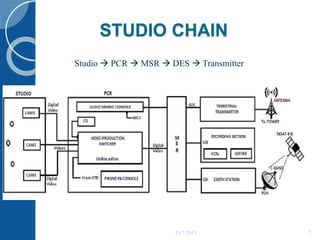
The document provides an overview of inplant training at Doordarshan Kendra and All India Radio in Thiruvananthapuram. It discusses the history and structure of DDK, including its two studios, terrestrial transmitters, and digital uplink station. It also explains the signal flow from studio to transmitter, covering components like the production control room, master switching room, digital earth station, and transmitter. For AIR, it outlines the radio network and describes the studio chain, control room, studio transmitter link, earth stations, and MW, SW and FM transmitters. The conclusion states that the training provided hands-on experience of the mass communication organizations and technologies used.