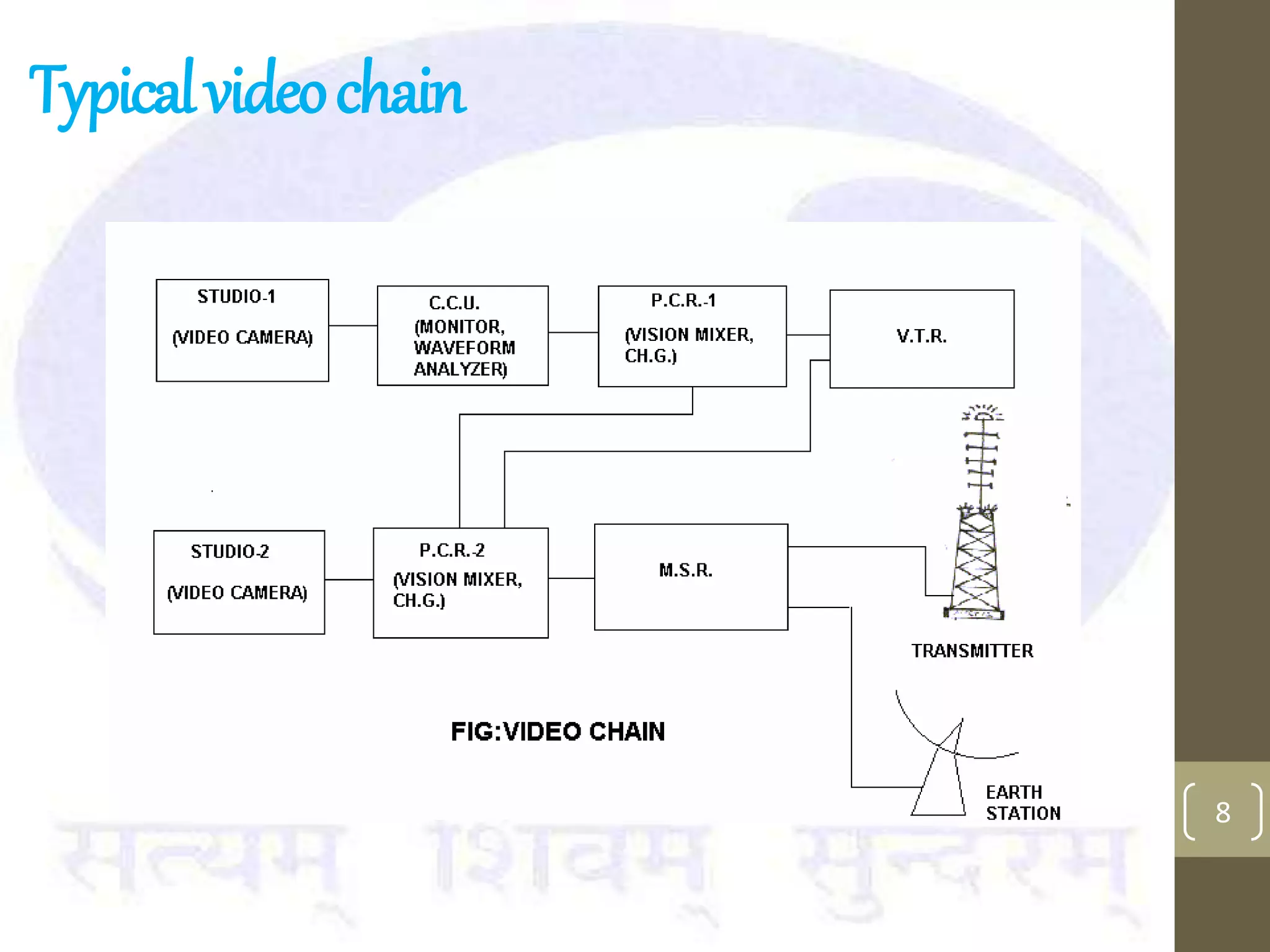
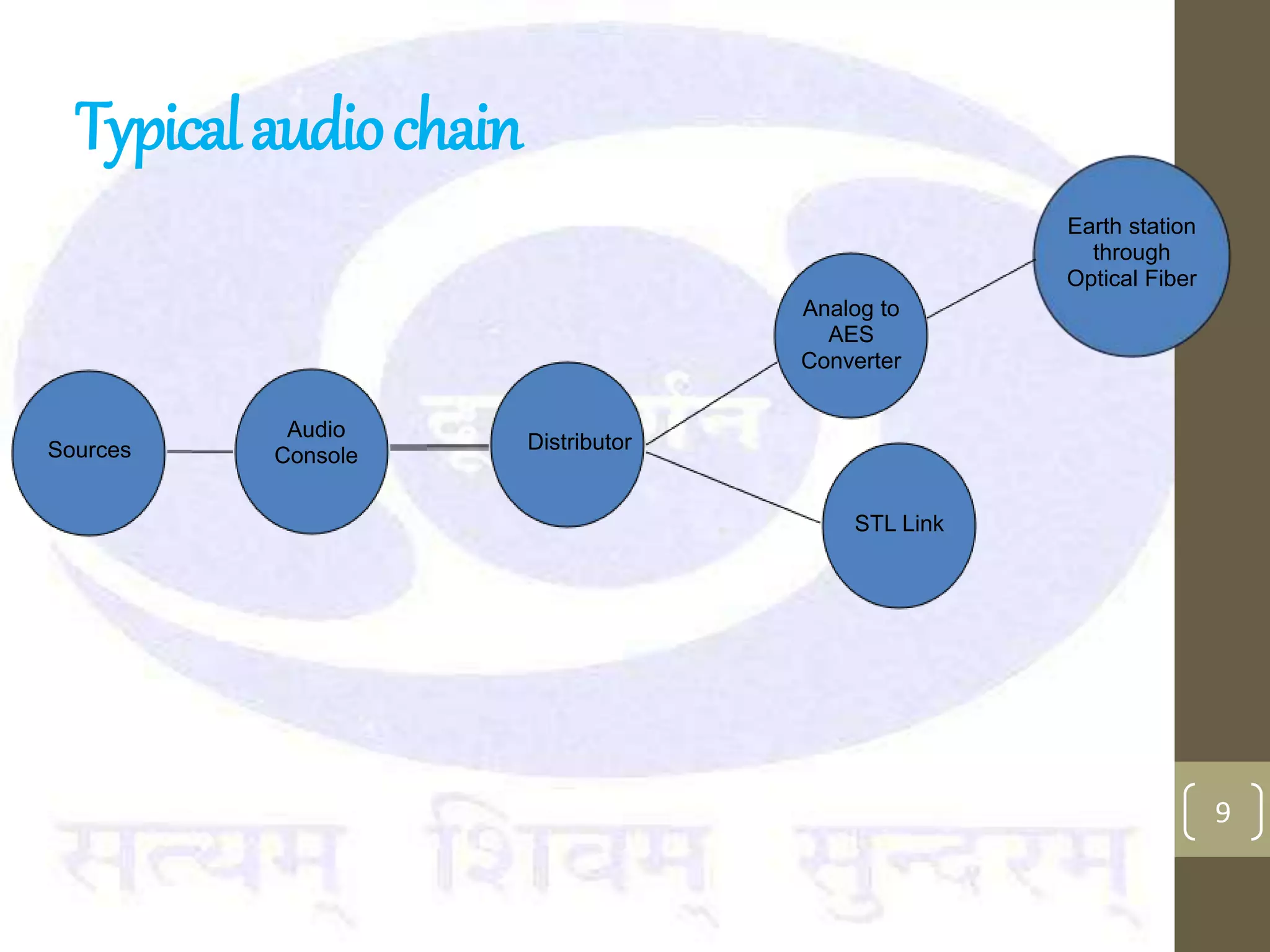
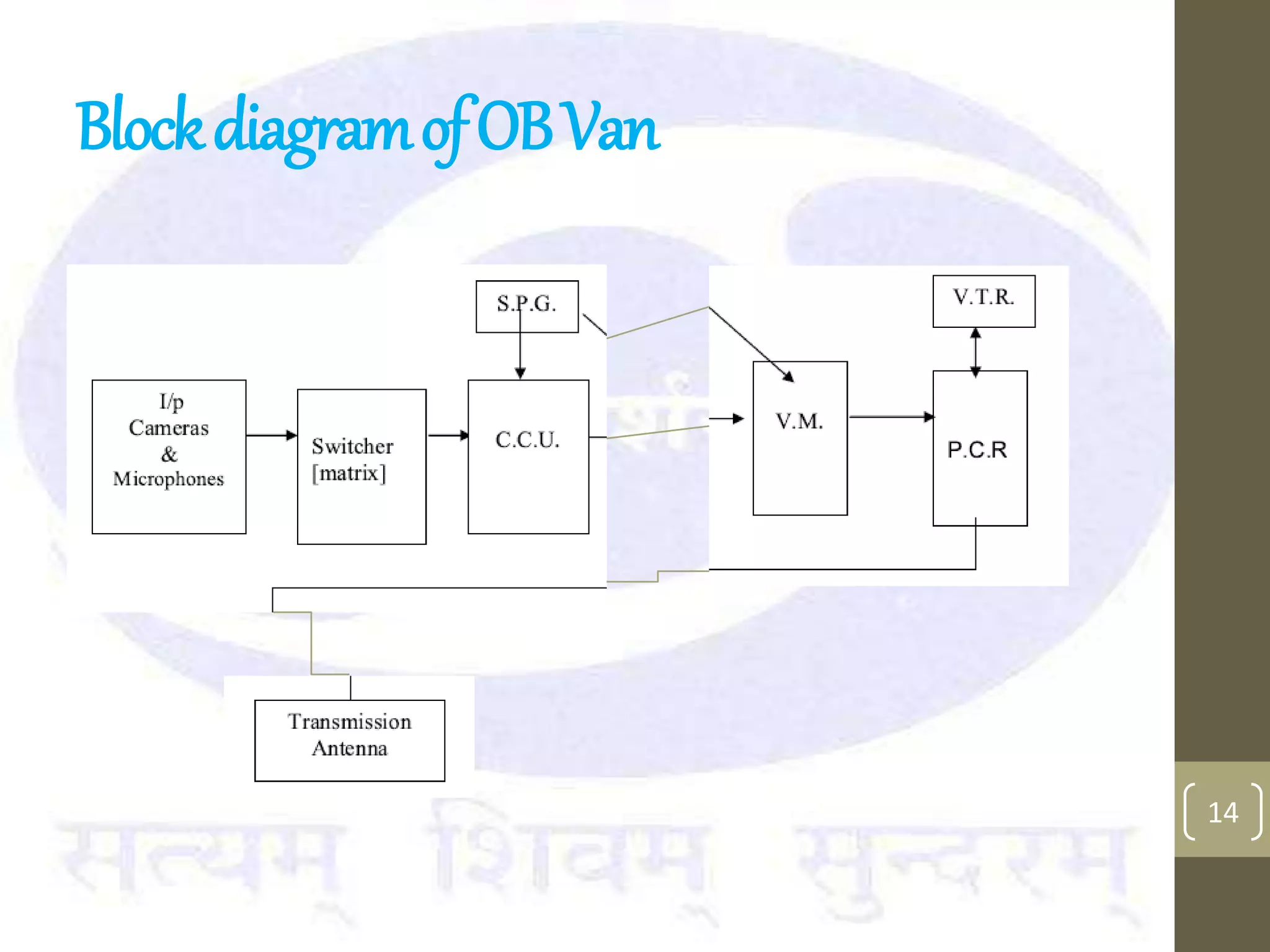
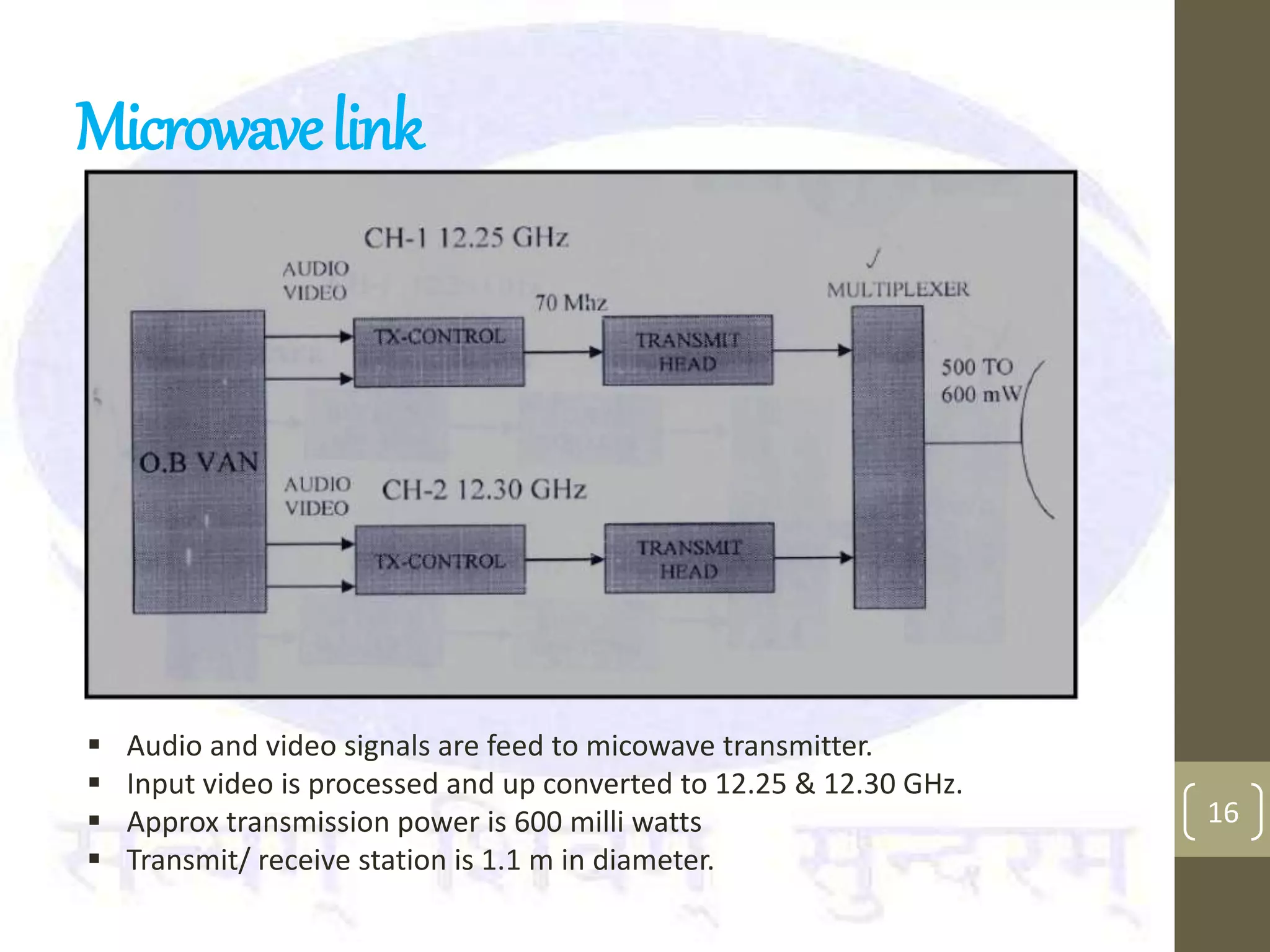
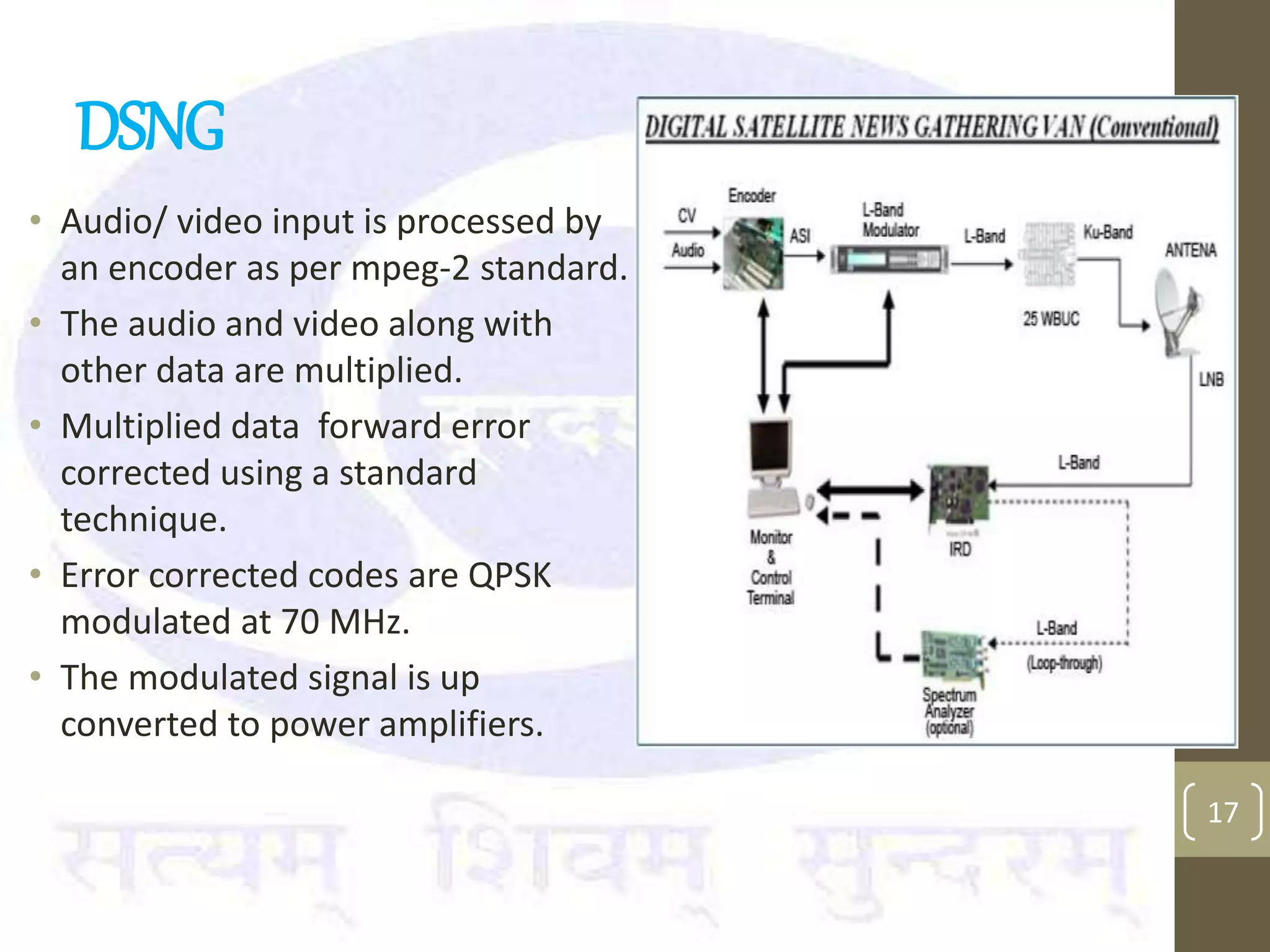
This document provides an overview of the components and processes involved in television broadcasting in India. It discusses the key elements of a television studio, including cameras, lighting, microphones, and a vision mixer to switch between video sources. It describes the typical video and audio chains used. The master switching room is discussed as housing most of the switching electronics. Earth stations are described as uplink centers that transmit signals to satellites for broadcasting to specified areas. Outside broadcasting vans are mobile studios used to broadcast news and sports events remotely. They include production, audio, video, and transmission areas. Microwave links and digital satellite news gathering are options for transmitting live signals from remote locations.