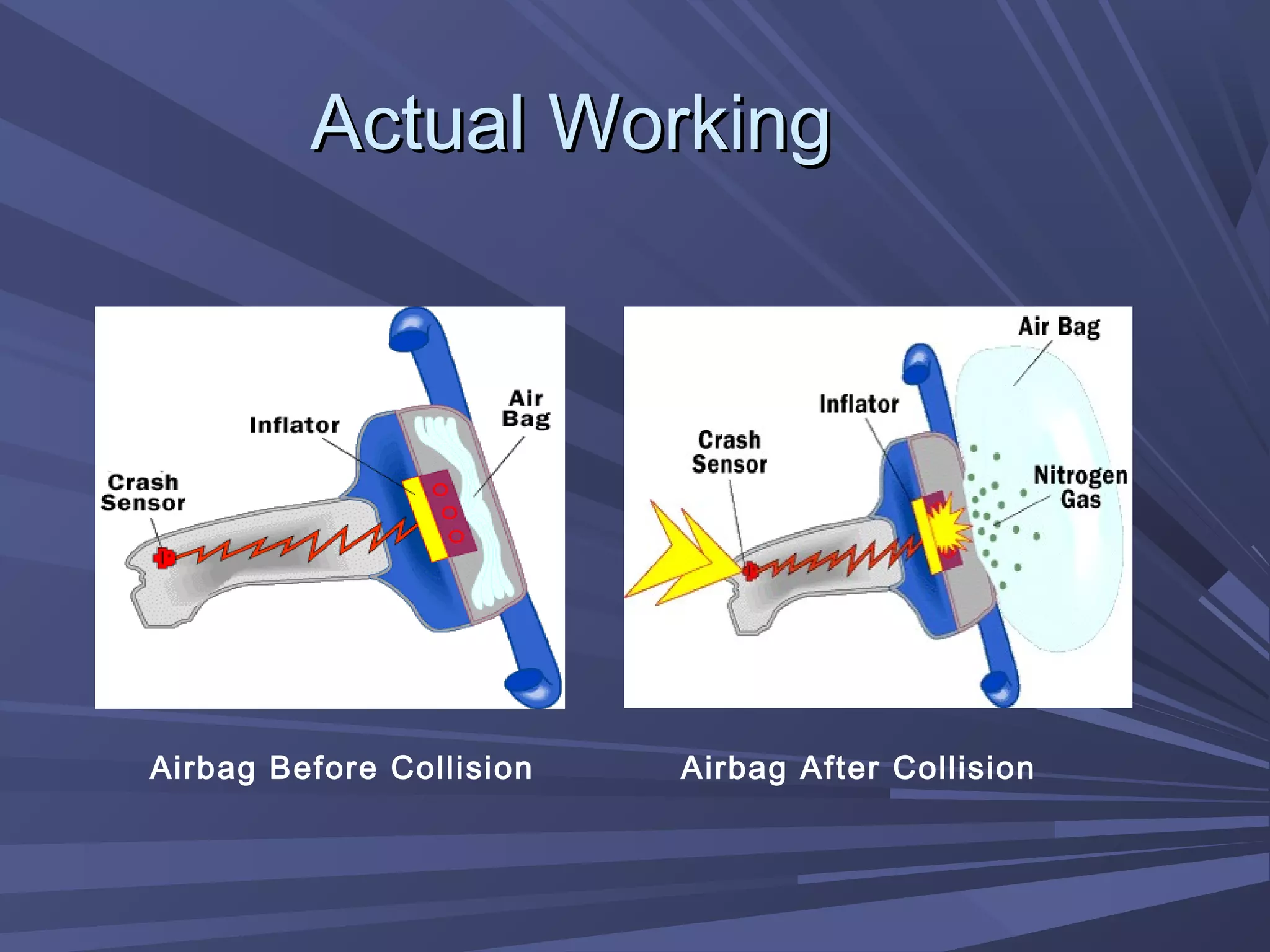
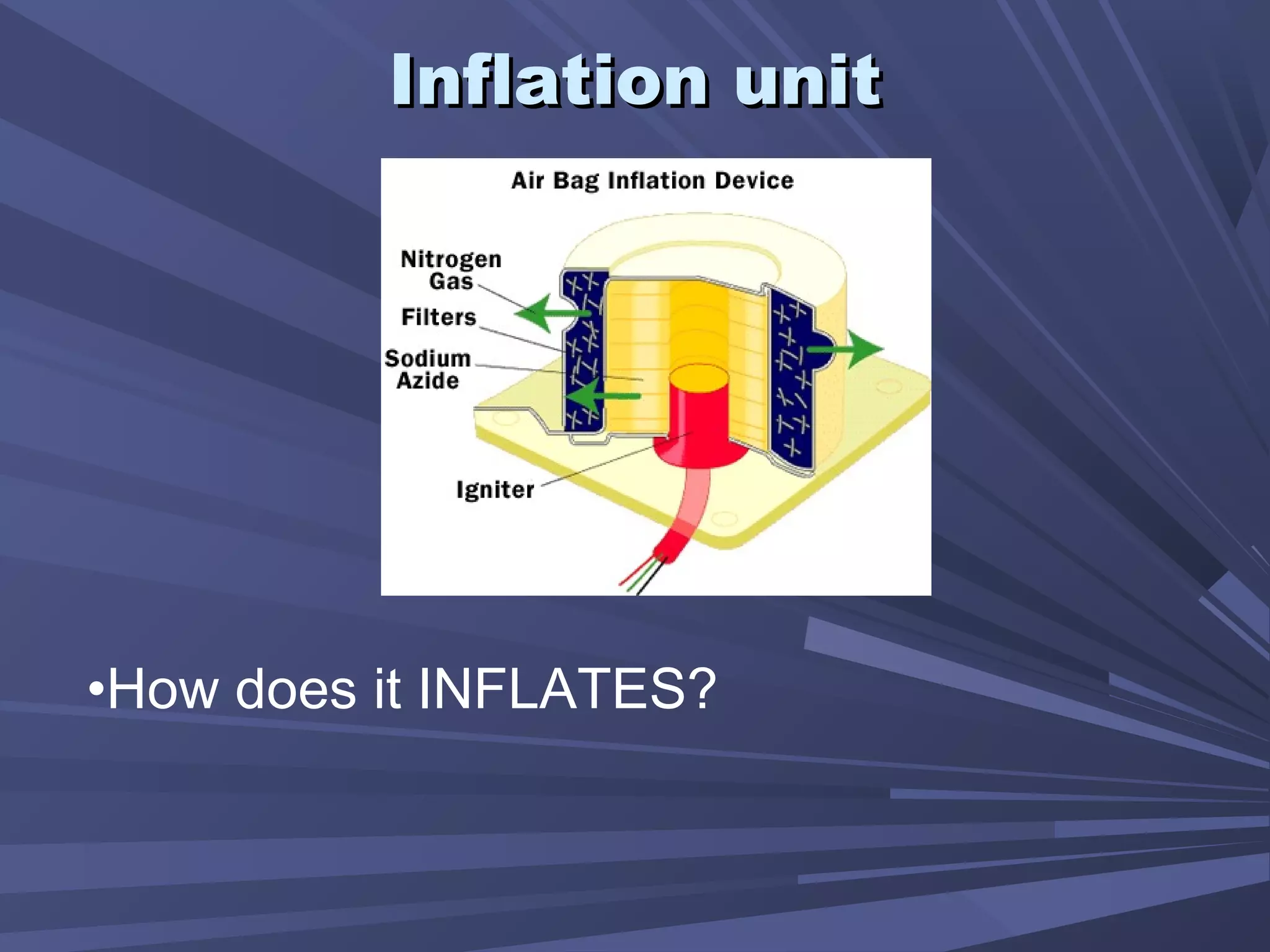
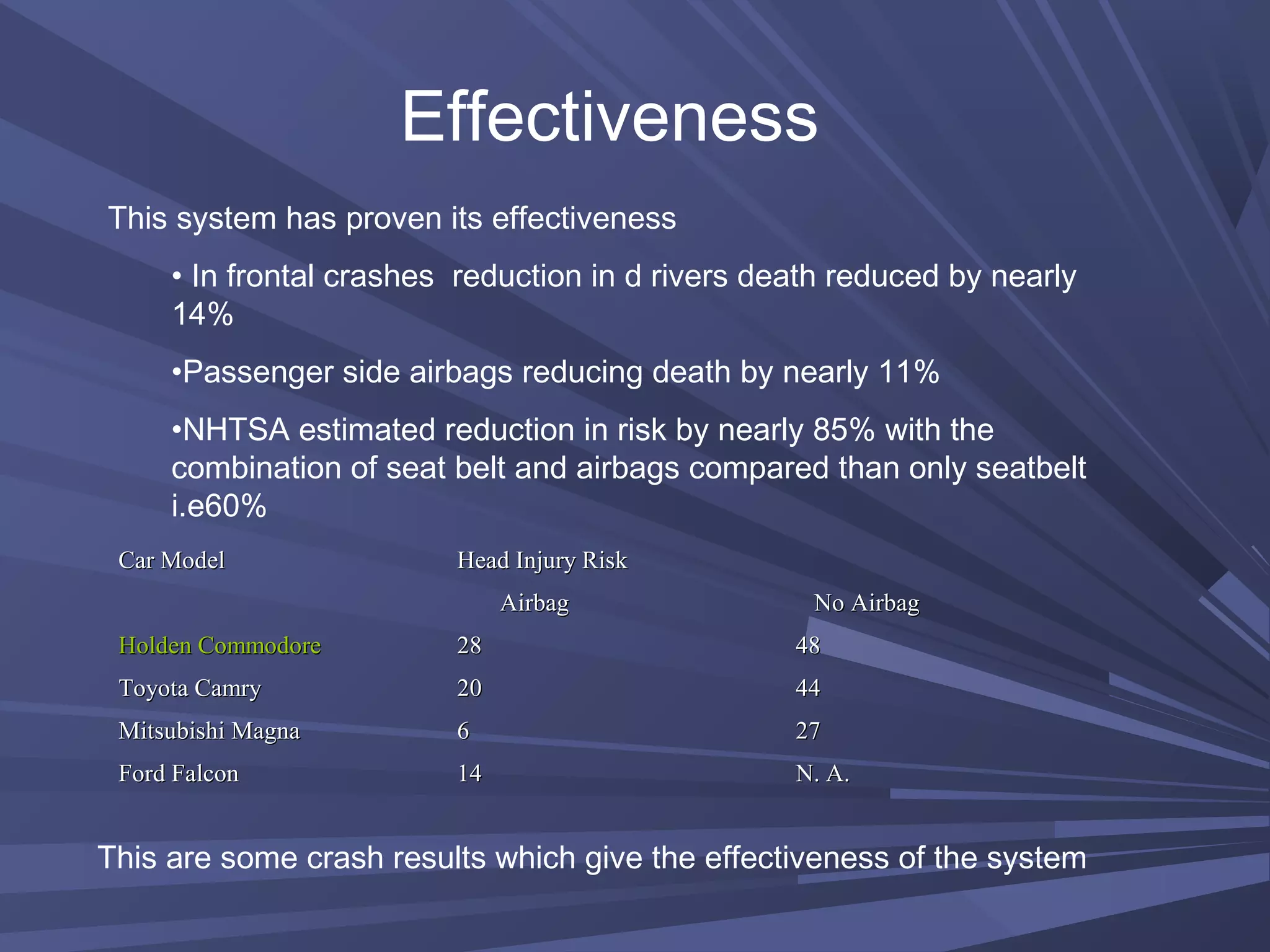
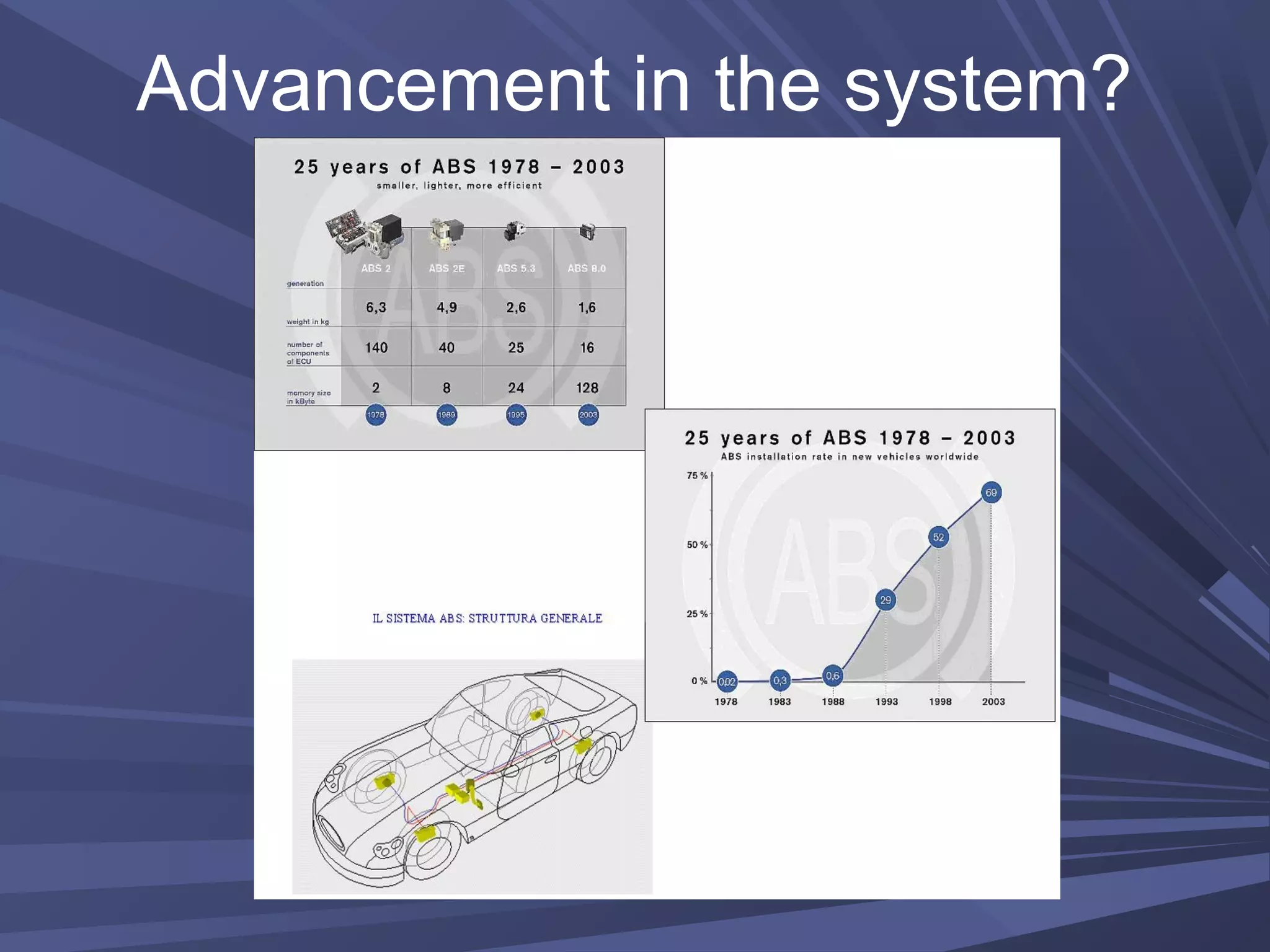
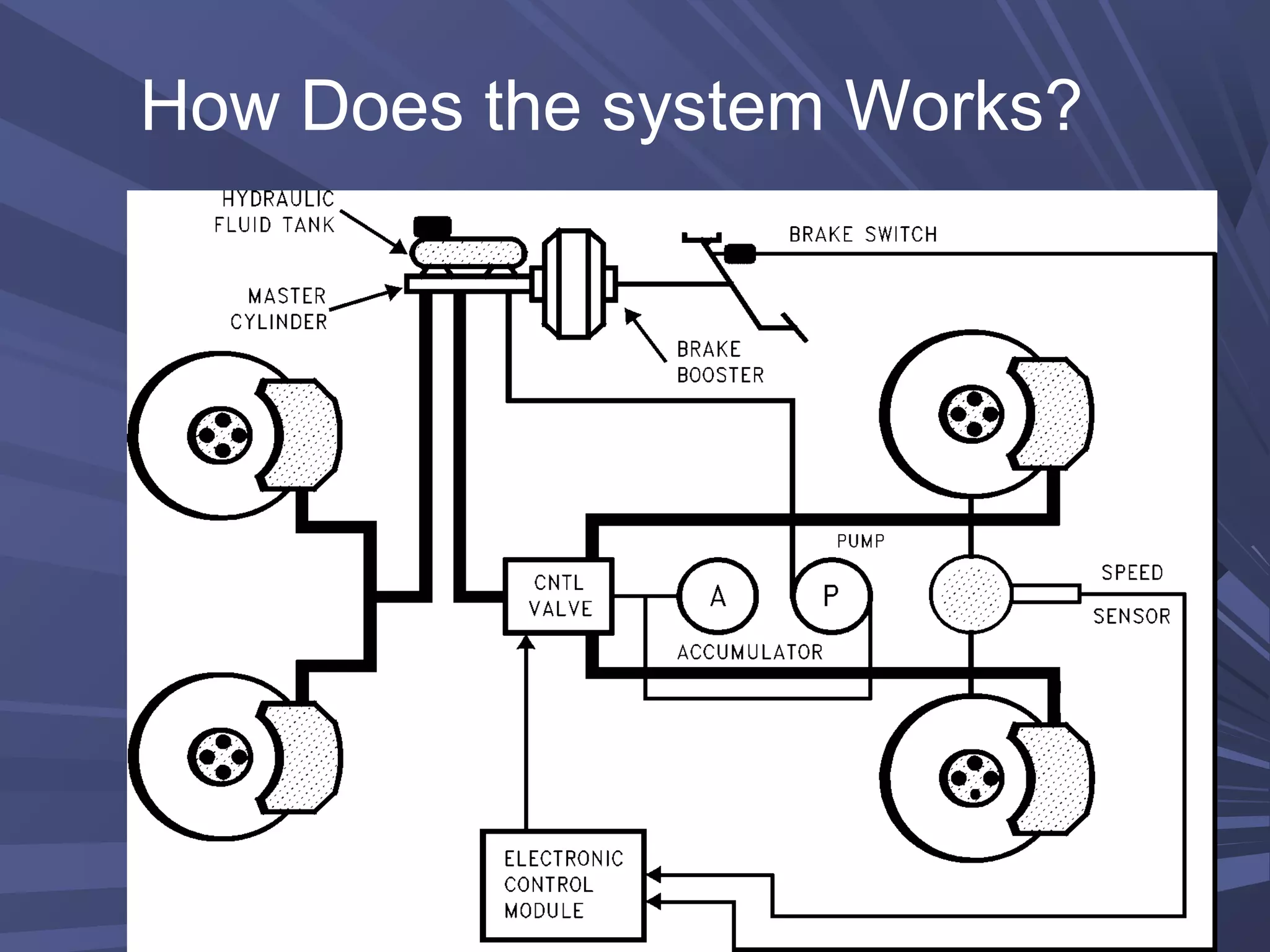
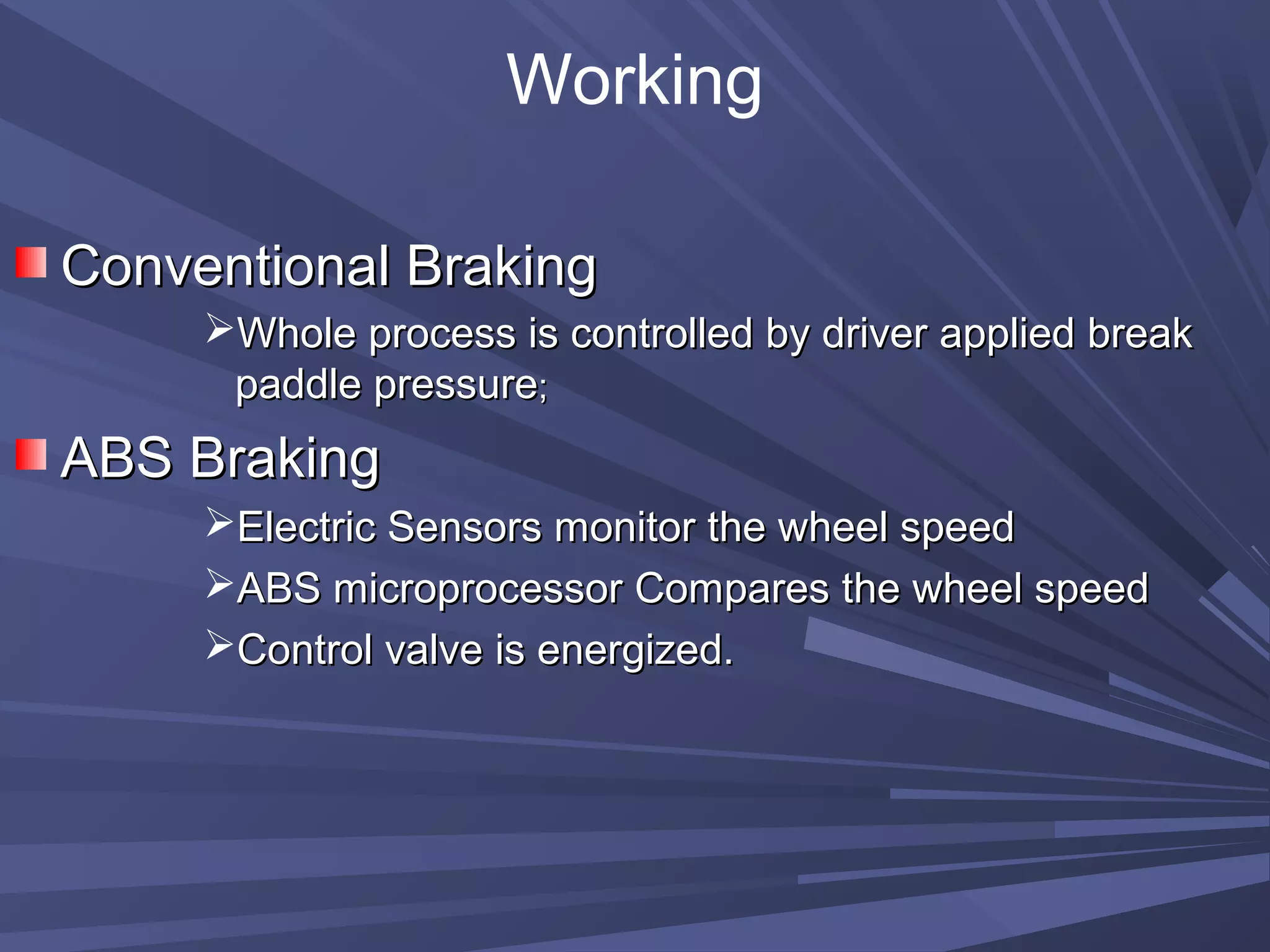
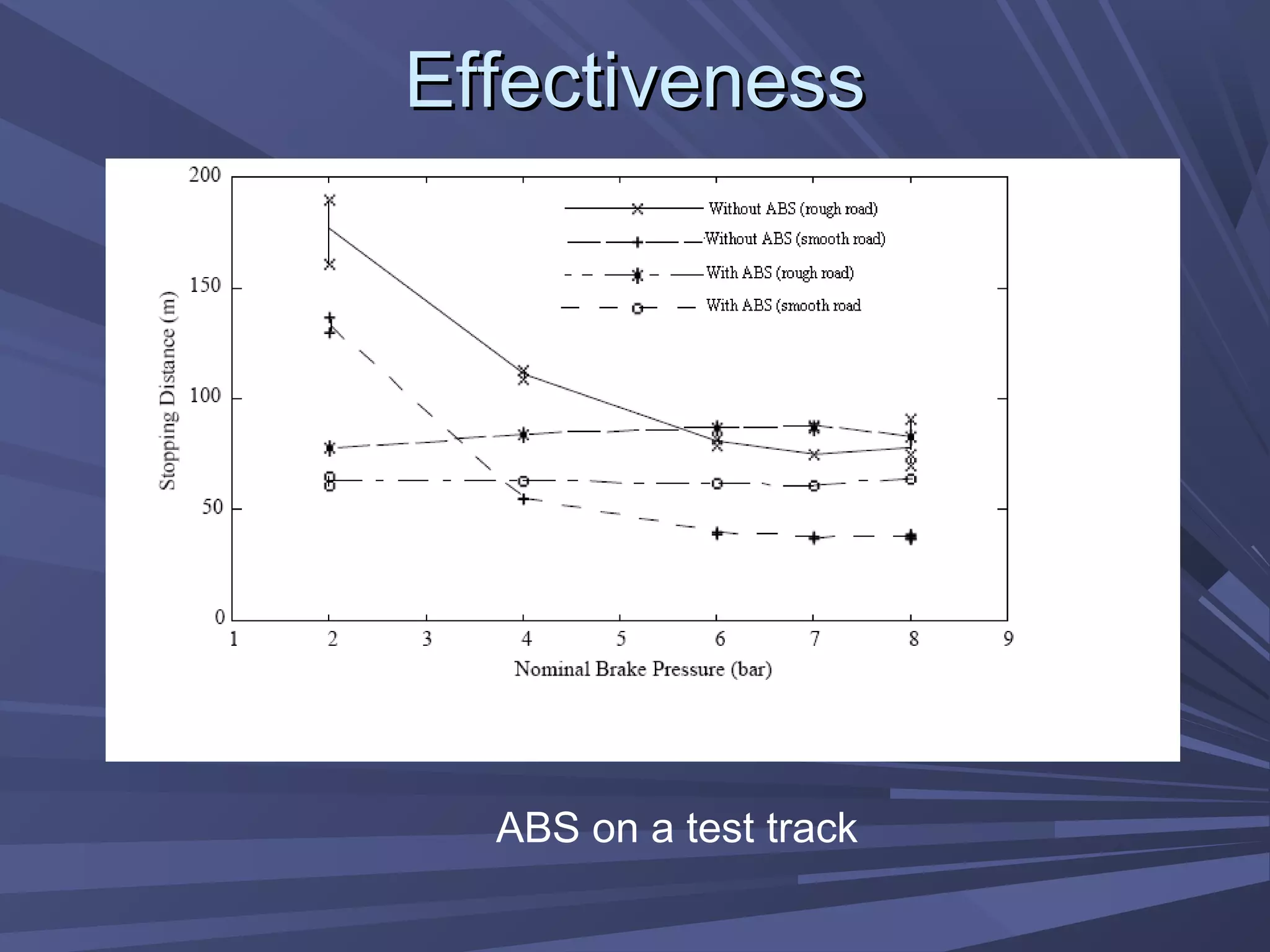
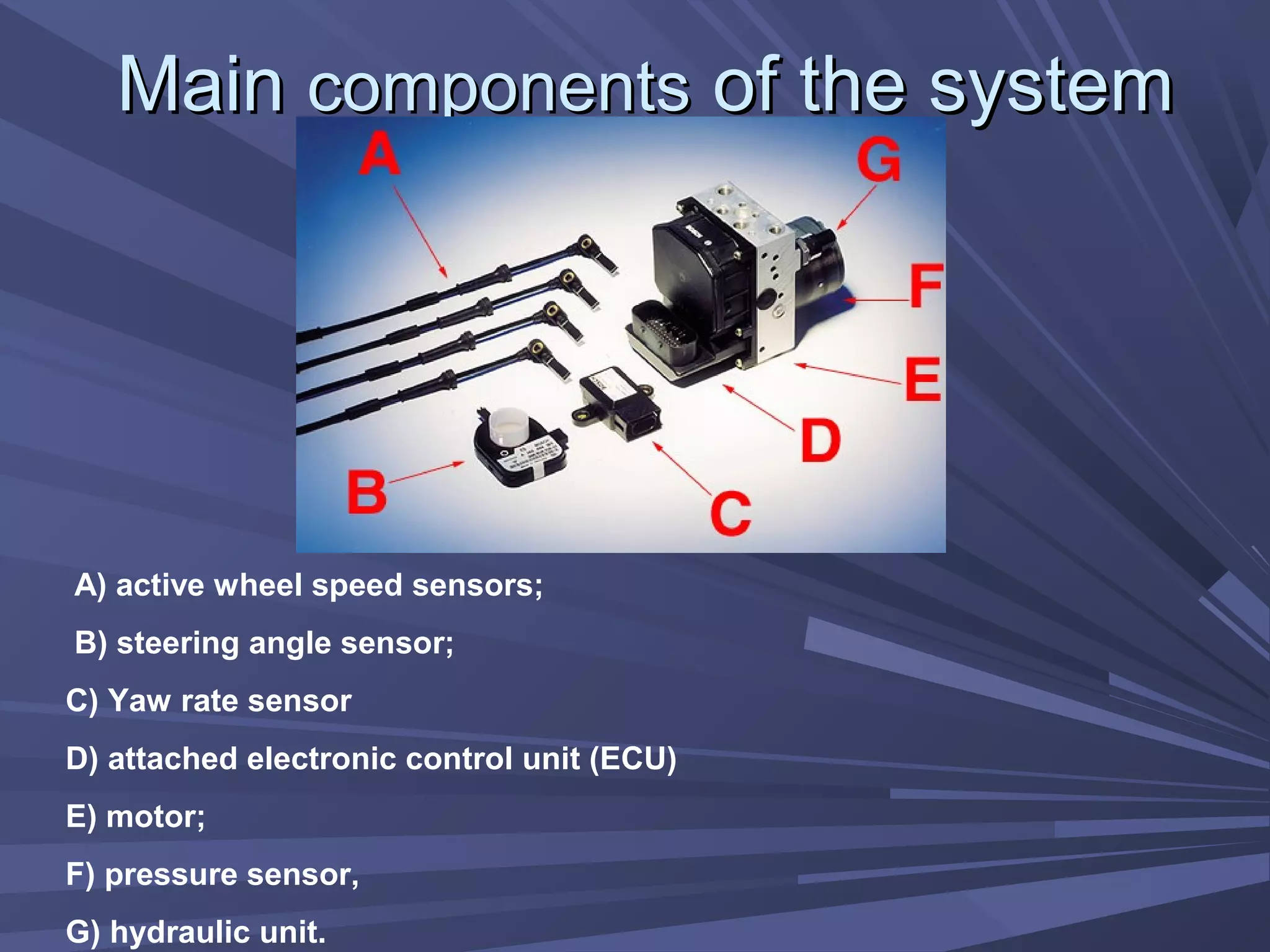
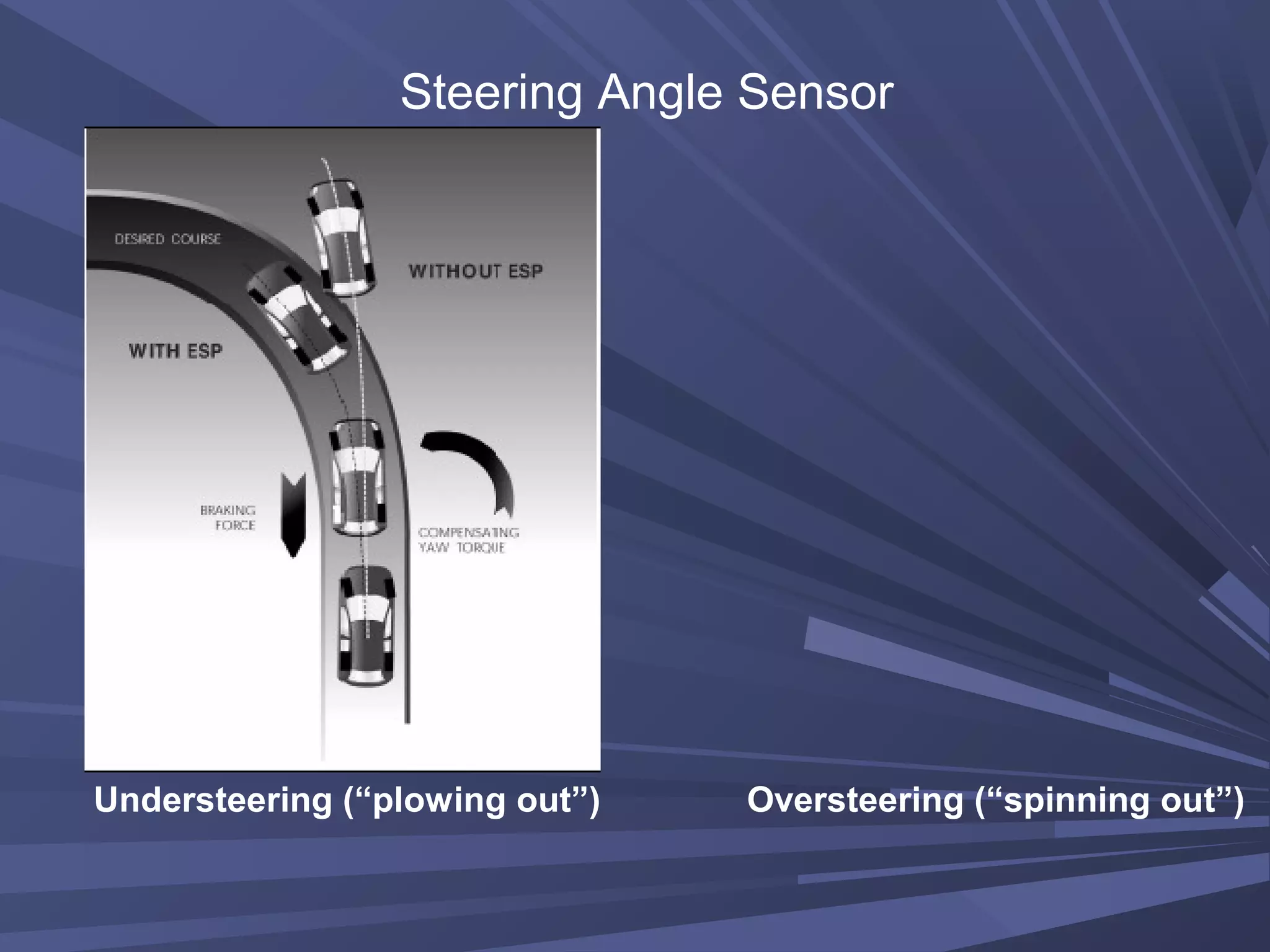
This document provides information on various automobile safety features, including airbags, anti-lock braking systems, traction control, and electronic stability control. It discusses how airbags work by inflating rapidly during a collision to cushion occupants from impact. Anti-lock braking systems use sensors and microprocessors to monitor wheel speed and prevent skidding during braking. Traction control builds on ABS to control engine and brake functions to prevent wheel slip on low traction surfaces. Electronic stability control uses sensors and individual braking of wheels to augment stability and correct understeering or oversteering situations. Global automakers spend billions annually on new safety technologies to protect occupants.