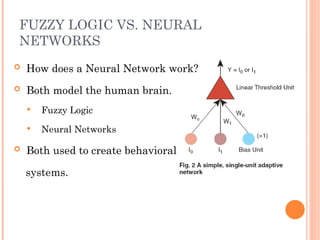
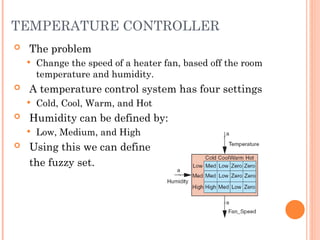
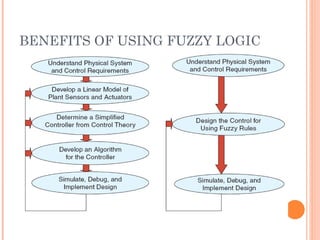
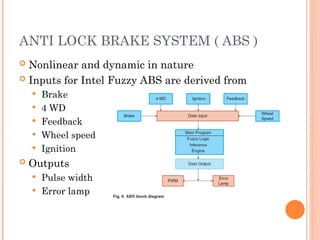
Fuzzy logic is a method of knowledge representation for concepts that are not precisely defined, originating from the ideas of Lotfi Zadeh in 1965. It contrasts with traditional logic by using fuzzy sets to handle degrees of truth, and is applied effectively in control systems like temperature controllers and anti-lock brake systems. Fuzzy logic is advantageous for its ability to represent subjective attributes and enhance the design process across various fields, including business and expert systems.



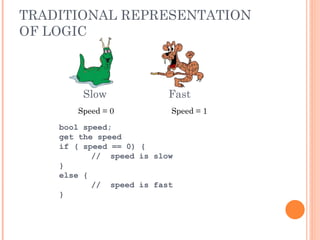
![FUZZY LOGIC REPRESENTATION
For every problem
must represent in
terms of fuzzy sets.
What are fuzzy
sets?
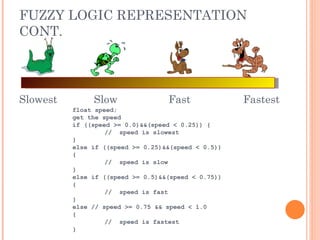
Slowest
Fastest
Slow
Fast
[ 0.0 – 0.25 ]
[ 0.25 – 0.50 ]
[ 0.50 – 0.75 ]
[ 0.75 – 1.00 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzylogic1-241210114136-4ccc791f/85/Fuzzy-Logic-full-powerpoint-lecture-fuzzy-5-320.jpg)