Embed presentation
Download as ODP, PPTX





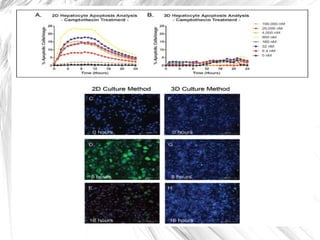


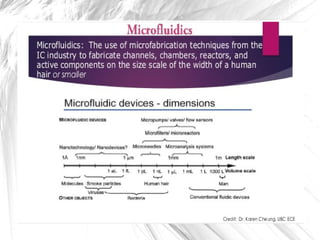


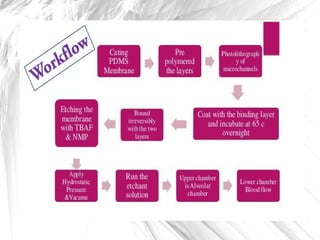
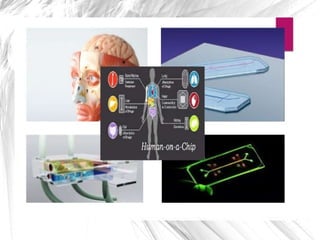
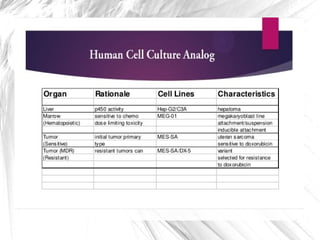


3D cell culture allows for more natural cell-to-cell attachments and communication through gap junctions compared to 2D culture. This results in greater tissue differentiation and resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs and radiation in 3D culture, whereas cells in 2D culture are more easily killed. A lab-on-a-chip integrates multiple laboratory functions onto a single microfluidic chip and offers advantages like lower reagent costs, portability, faster reactions, and lower fabrication costs compared to traditional labs.














