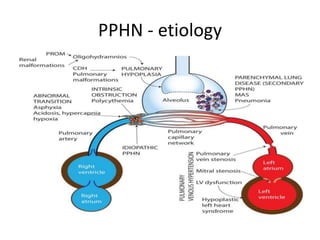
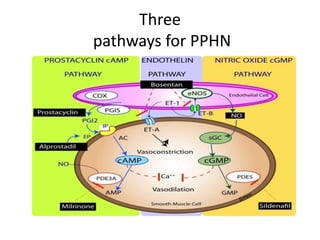
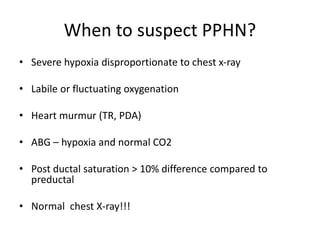
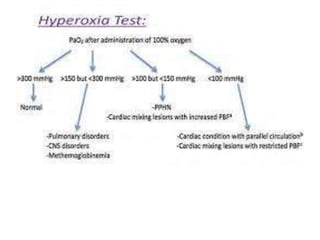
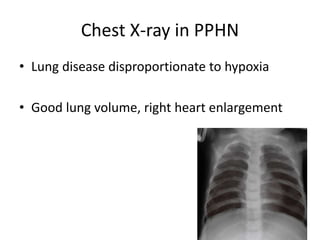
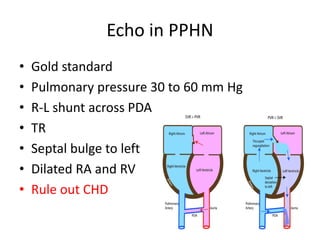
This document discusses persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). It begins by describing the normal fetal to neonatal circulation transition at birth. PPHN occurs when the pulmonary hypertension persists, causing severe hypoxia. There are three types of PPHN based on etiology: maladaptation, underdevelopment, and maldevelopment. Management involves three steps - relieving pulmonary vasoconstriction with supportive measures, recruiting alveoli through ventilation techniques, and using pulmonary vasodilators like inhaled nitric oxide. Echocardiography is important for diagnosis and shows three key findings - increased pulmonary pressures, tricuspid regurgitation, and septal wall abnormalities. The prognosis depends on severity, with mortality