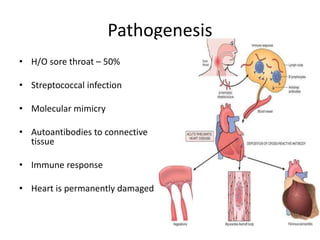
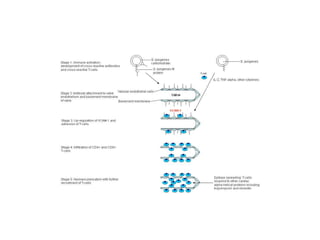
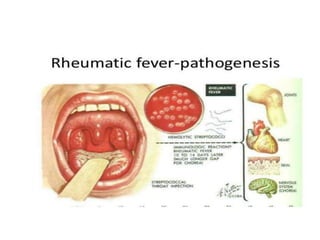
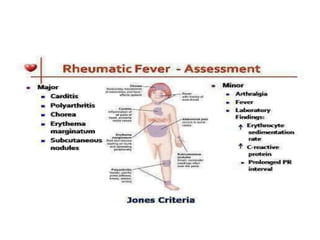
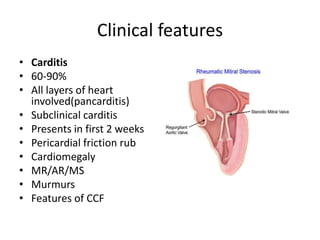
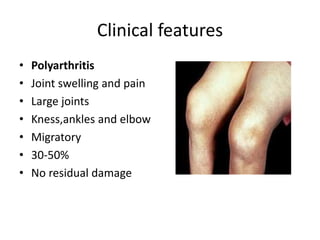
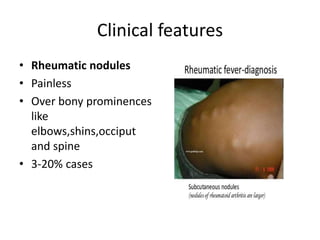
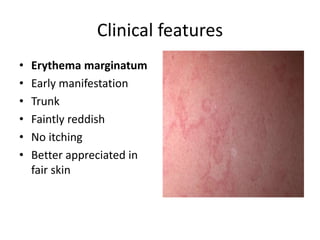
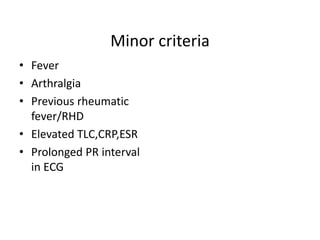
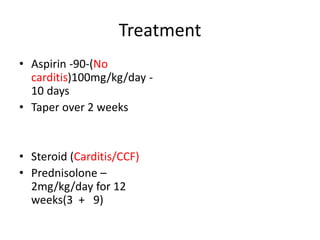
Rheumatic Fever is an immunological disorder that follows streptococcal infection and can lead to rheumatic heart disease. It most commonly affects children between 5-15 years of age and is more prevalent in populations with poor socioeconomic status. The pathogenesis involves molecular mimicry between streptococcal antigens and heart tissues, resulting in autoimmune damage to the heart valves. Clinical features include carditis, polyarthritis, chorea, and subcutaneous nodules. Treatment involves bed rest, antibiotics, aspirin, and steroids. Primary prevention focuses on early treatment of streptococcal infections, while secondary prophylaxis uses long-term benzathine penicillin injections.