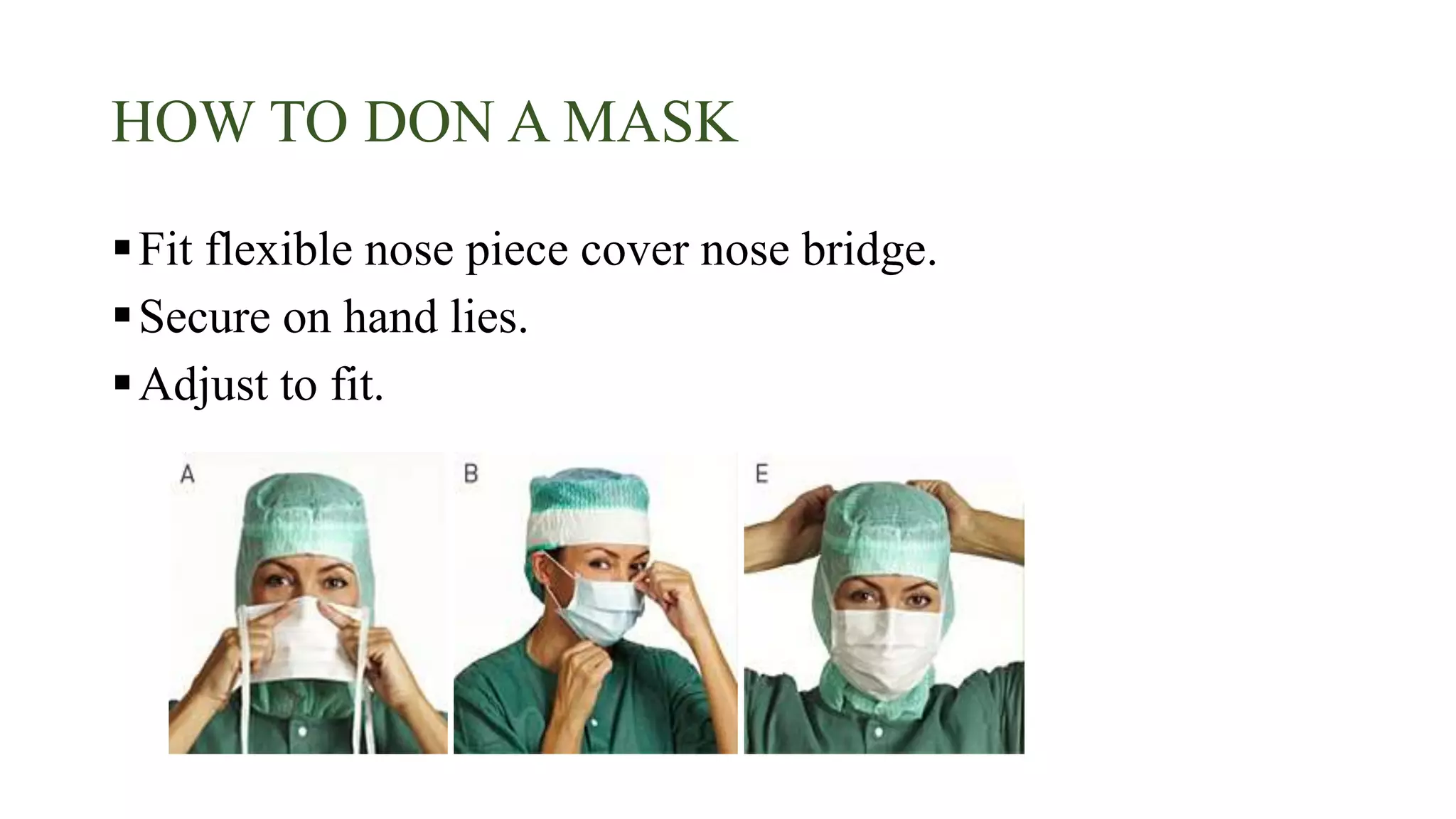
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is clothing and equipment designed to protect the wearer from health and safety risks. As a nurse, using proper PPE is important for preventing the transmission of infections. The types of PPE include respiratory protection, eye protection, gloves, gowns, and protective clothing for other parts of the body. When using PPE, it is essential to select the correct type for the task and ensure proper fitting. PPE should be donned before entering a patient's room and removed carefully while following hand hygiene procedures to prevent the spread of contamination.




















![GLOVES
ALWAYES WEAR GLOVES WHEN,
• Direct contact with body fluids is anticipated [ nose bleeds,
bleeding, abrasions, et.,,]
• Handling clothes solid by urine ,faeces, vomit, or blood
• Diapering children.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppe-190102170357/75/PPE-22-2048.jpg)