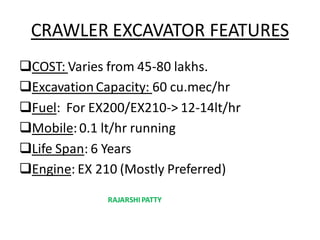
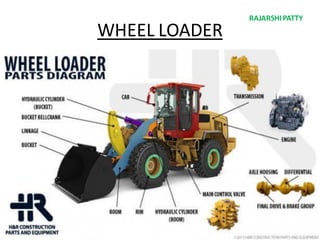
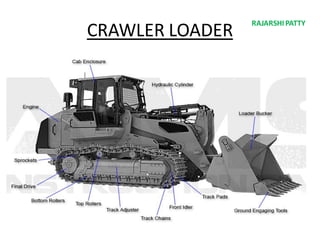
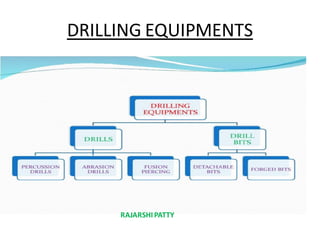
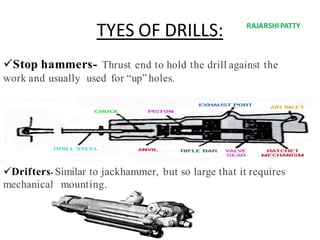
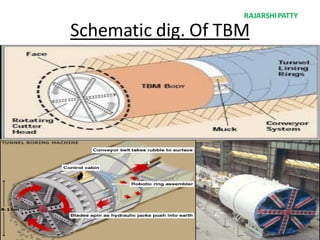
The document provides a comprehensive overview of tunneling and rock drilling equipment, detailing the definitions, history, reasons for tunnel construction, advantages, and types of tunnels. It outlines various methods of tunnel construction, drilling equipment, and the specific tools and explosives used in the tunneling process. Additionally, it includes information about tunnel boring machines and their features, advantages, and disadvantages.