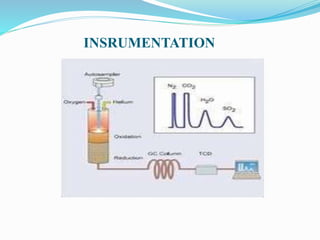
This document discusses the principles and applications of CHNS elemental analyzers. CHNS analyzers determine the levels of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur in organic materials through combustion. Samples are burned at high temperatures, converting the elements to gases that are then detected using techniques like gas chromatography or thermal conductivity. The instruments are used widely in fields like pharmaceuticals, polymers, chemicals, foods, and oil refining to analyze sample composition and monitor processes.