Embed presentation
Download to read offline












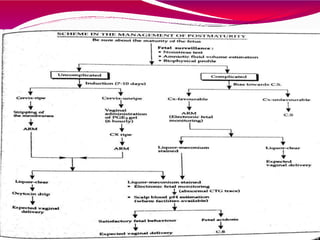

This document discusses post-maturity or post-term pregnancy, which is defined as pregnancy continuing beyond 294 days (42 completed weeks) from the last menstrual period. The incidence of post-term pregnancy ranges from 4-14%, with an average of about 10%. Potential causes include incorrect dating, biological variability, and maternal factors like primiparity or previous post-term pregnancy. Diagnosis involves assessing the menstrual history and clinical findings. Investigations to confirm fetal maturity and detect placental insufficiency include ultrasound, amniocentesis, and x-rays. Fetal wellbeing is assessed using tests like NST, biophysical profile, ultrasound for amniotic fluid index, and Doppler. Complications for the fetus include













