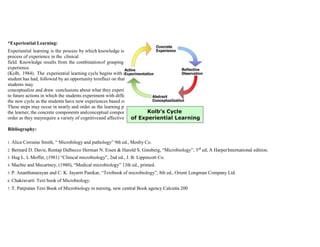
This document outlines a course on Applied Microbiology and Infection Control including Safety. The course is divided into two sections - Applied Microbiology and Infection Control & Safety. The Applied Microbiology section focuses on classification, identification, and mechanisms of disease-causing microorganisms. The Infection Control & Safety section teaches practices for preventing healthcare-associated infections, appropriate use of personal protective equipment, disinfection/sterilization, and patient and employee safety protocols. The course utilizes lectures, demonstrations, discussions, and experiential learning to help students develop relevant competencies in microbiology and infection control.