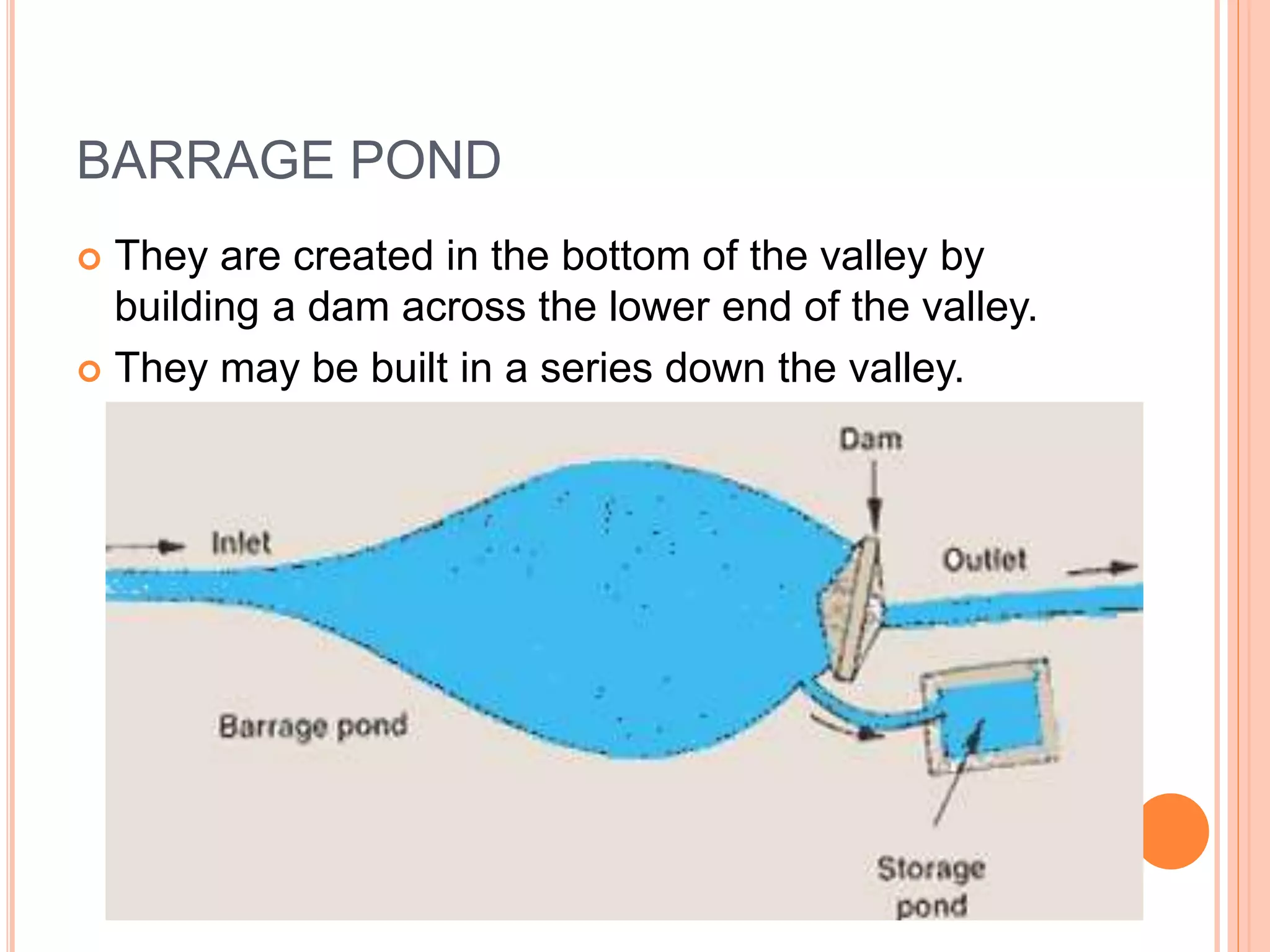
This document describes different types of ponds. There are three basic types: sunken ponds, which are below the surrounding land level and fed by groundwater; barrage ponds, which are created by building dams across valleys; and diversion ponds, which are fed indirectly from other water sources through canals. Ponds can also be classified by their construction materials as earthen, walled, or lined. Their construction method determines if they are dug out, use embankments, or are cut and fill types. Earthen ponds constructed solely with soil materials are the most common.