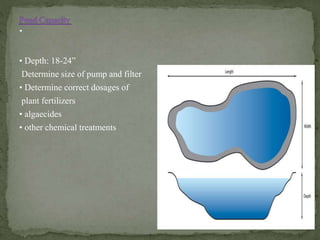
A water garden is a designed space featuring aquatic plants, originating in ancient Egypt with sacred lotuses. Water gardens serve both aesthetic and functional purposes, offering various types such as ponds, fountains, waterfalls, and streams, and have historical significance in cultures including Mughal and Japanese gardens. The document also discusses the components of ecosystem ponds, the benefits of incorporating fish, and modern trends in water garden design.