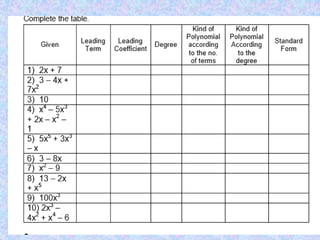
The document defines key terms related to algebraic expressions. It states that a term is a constant, variable, or product of a constant and variable. The numerical coefficient is the constant number and literal coefficient is the variable and its exponent. A polynomial is an algebraic expression where each term has a whole number exponent. It classifies polynomials based on number of terms (monomial, binomial, trinomial) and degree (constant, linear, quadratic). The standard form arranges terms from highest to lowest degree with the leading term having the highest degree.