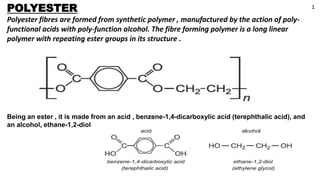
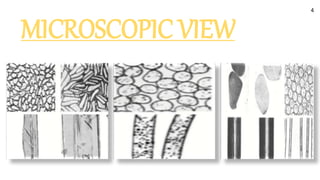
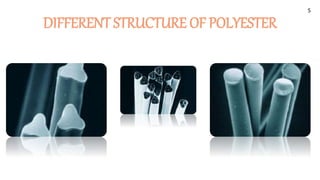
The document provides a comprehensive overview of polyester fibers, covering their introduction, manufacturing process, and characteristics including physical, chemical, and thermal properties. It explains the different forms of polyester and their structure, appearance, and performance, highlighting their durability, resistance to environmental factors, and suitability for various applications. The document also details the effects of various substances and conditions on polyester, asserting its stability and ease of use in textile engineering.