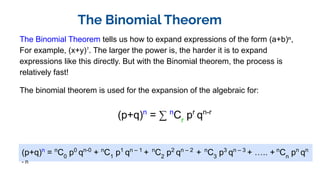
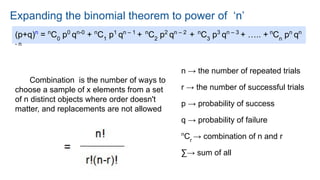
The document explains the binomial theorem, which facilitates the expansion of expressions like (a+b)^n, and discusses the binomial distribution representing trials with binary outcomes (success or failure). It also covers the poisson distribution, focusing on its application to predict the probability of events occurring within a specific interval, with notable applications in various fields such as call centers, website traffic, and banking. The historical origins of both distributions are briefly outlined, highlighting key contributors like Isaac Newton for the binomial theorem and Siméon-Denis Poisson for the poisson distribution.