This physics document discusses several topics:
1) Conduction, convection, and radiation are the three mechanisms of heat transfer. Conduction involves transfer through direct contact, convection involves transfer by fluid currents, and radiation involves infrared wave emission.
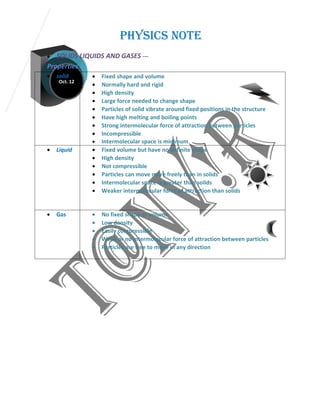
2) Solids have a fixed shape and volume, liquids have a fixed volume but no shape, and gases have no fixed shape or volume. Solids have the highest density while gases have the lowest.
3) Other topics covered include work, energy, types of potential energy, density, pressure, and the properties of solids, liquids, and gases.
![Physics note
• Conduction ---conduction is the transfer of thermal energy without any flow of the
medium.
o Or, conduction is the transfer of thermal energy through a substance without the
substance itself moving.
• 2Oct. 12
mechanisms –molecular vibration and free electron vibration
• Solid [metals] are good conductors of heat while liquids and gases are poor conductors
of heat.
• Insulators---objects that cannot conduct heat well are called insulators
o Or, materials that are poor conductors of heat are called insulators. E.g. glass,
wood etc.
• Convection---it is the transfer of thermal energy by means of currents in the material
medium [liquid or glass]
o Or, convection is the transfer of heat through fluids [liquid or gas] by the upward
movement of warmer less dense regions of the fluid.
• Convection current ---Convection current is the movement of fluids caused by the
change in densities in various parts of the fluid.
• Radiation ---thermal radiation is the transfer of energy by infra- red [IR] waves.
o Or, radiation is the continual emission of infra – red waves from the surface of all
bodies, transmitted through space without the aid of material medium.
• Dull black surfaces are better emitters of infra – red radiation than shiny, white surfaces.
• The higher the surface temperature, the higher the rate of transfer of energy by
radiation.
• Work –work done by a constant force is given by the product of the force and the
distance moved in the direction of force
o Therefore, work done = force applied ×distance through the direction of the force
• [In joules, j] [In Newton, N] [In metre, m]
• Energy --- energy is the ability of a body to do work
Or, energy is defined as the capacity o9f a body to do work.
• Forms of energy ----
• Kinetic energy – this is the energy due to motion. All moving objects have kinetic energy.
• Potential energy –this is the energy which an object has because of its position, shape or state.
• Types of potential energy ---
• Gravitational potential energy --- this is the energy that an object possesses because of its
position above the ground.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conduction-120921133824-phpapp01/75/Conduction-by-T-NV-R-Ahmed-1-2048.jpg)
![Physics note
• Elastic potential energy --- this is the energy possessed by an stretched spring or rubber. Both of
them can do work when released.
• Chemical potential energy --- the energy stored in fuels, batteries, food etc is called chemical
potential energy. When they are burnt, they release energy by chemical reactions.
• Electrical potential energy --- electrons can transfer energy from a battery to a light bulb. They
Oct. 12
have electrical potential energy or electrical energy for short.
• Nuclear energy ---this is the energy released by the nucleus of an atom when the nucleus splits.
• Other types of energy ---
• Thermal energy—when hot objects cool down, their atoms and molecules slow down and lose
energy. This is known as thermal energy.
• Radiated energy – the sun radiates light. Loudspeakers radiate sound. Light and sound both
travel in the form of waves. These carry energy.
• Power -- powers defined as the rate of work done or energy converted.
in equation form,
• P = W/T = E/T
• One watt is defined as the rate of working or energy conversion of one joule
per second.
• DENSITY AND PRESSURE ---
• DENSITY --- the density of an object is its mass per unit volume
Density = mass ÷ volume
The SI unit of density is kilogram per cubic metre [kg/ m3]
• Pressure --- pressure is the force acting per unit area.
Pressure = force ÷ area
The SI unit for pressure is Pascal [Pa].
• Pressure increases with depth.
• The liquid will always settle to a common level.
The pressure at the base of a liquid column ---
P=ρ×g×h
• Where, p = pressure
ρ = density
g =gravitational field strength
h = height of the column
• Applications of transmission of pressure ---
• Hydraulic press.
• Hydraulic brakes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conduction-120921133824-phpapp01/85/Conduction-by-T-NV-R-Ahmed-2-320.jpg)