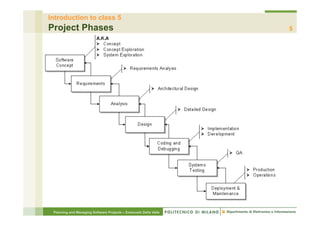
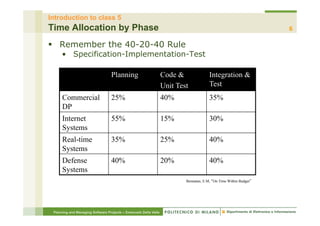
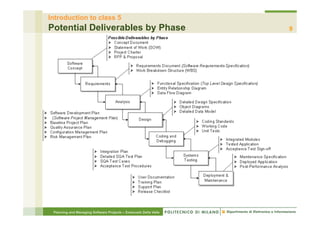
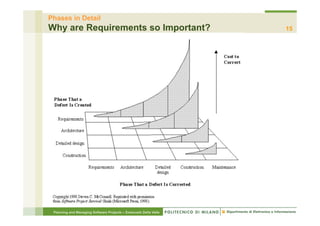
This document provides an overview of the planning phase and project lifecycles for software projects. It discusses the typical phases of a project including concept exploration, requirements, analysis and design, development, integration and testing, and deployment. It also describes different lifecycle models like waterfall and iterative development. The document is intended to teach project managers about establishing a project plan and selecting an appropriate lifecycle model.