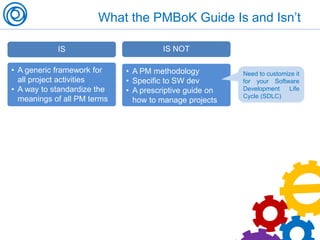
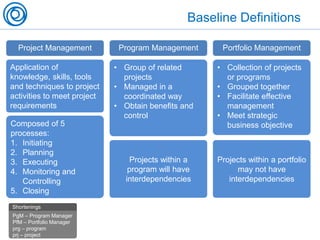
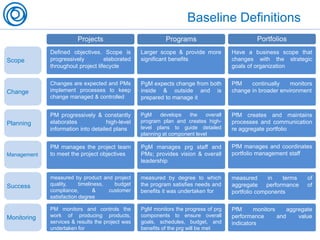
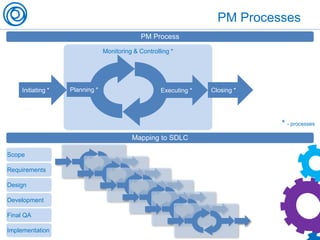
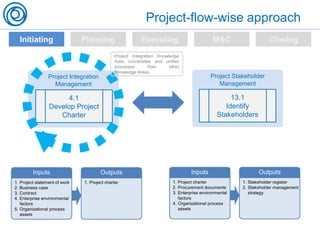
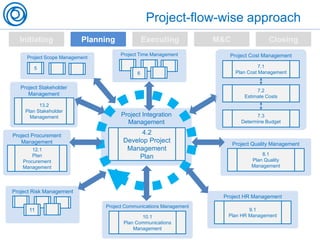
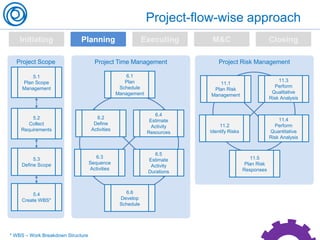
The document is a cheat sheet summarizing the PMBOK Guide (5th edition) and its application in project management, particularly in software development. It outlines the five main processes: initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing, as well as definitions of portfolio and program management. The author emphasizes the need for customization according to specific project needs and highlights the importance of managing changes in projects and programs.