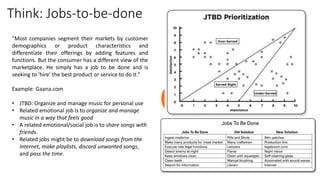
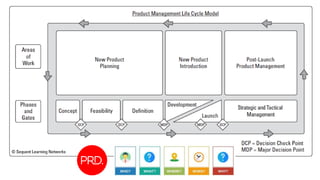
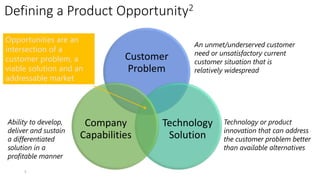
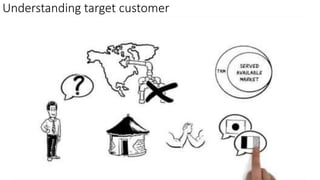
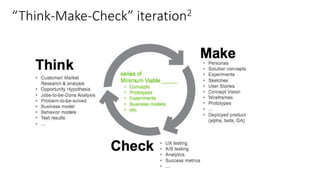
The document provides an overview of the product management lifecycle and role. It discusses defining product opportunities by understanding customer problems, technology solutions, and a company's capabilities. It also covers product discovery frameworks like minimum viable products and jobs-to-be-done. The agenda includes understanding customers, creating personas and wireframes, using analytics to check hypotheses, and approaching typical PM interview questions with a focus on structured thinking.










![IRCTC having flight booking
• I/we believe [target market] will [do this action / use this
solution] for [this reason]
• I believe that people booking train ticket will book flight since they
are not able to get a train ticket. What’s wrong?
• What MVP will you build to test your hypothesis?
• Post launch: How will we measure success of this product?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmworkshopv4-211011042412/85/PM-workshop-16-320.jpg)