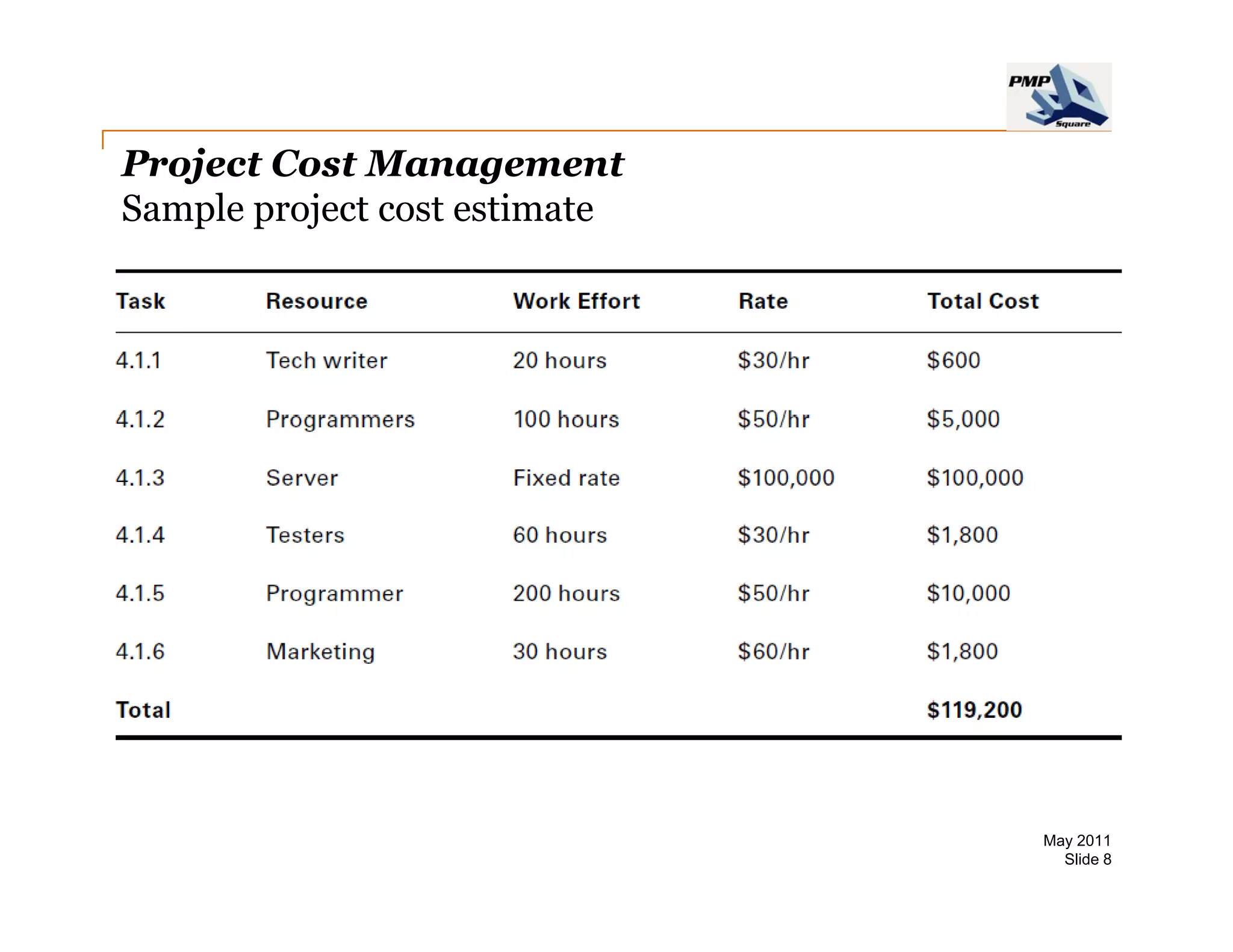
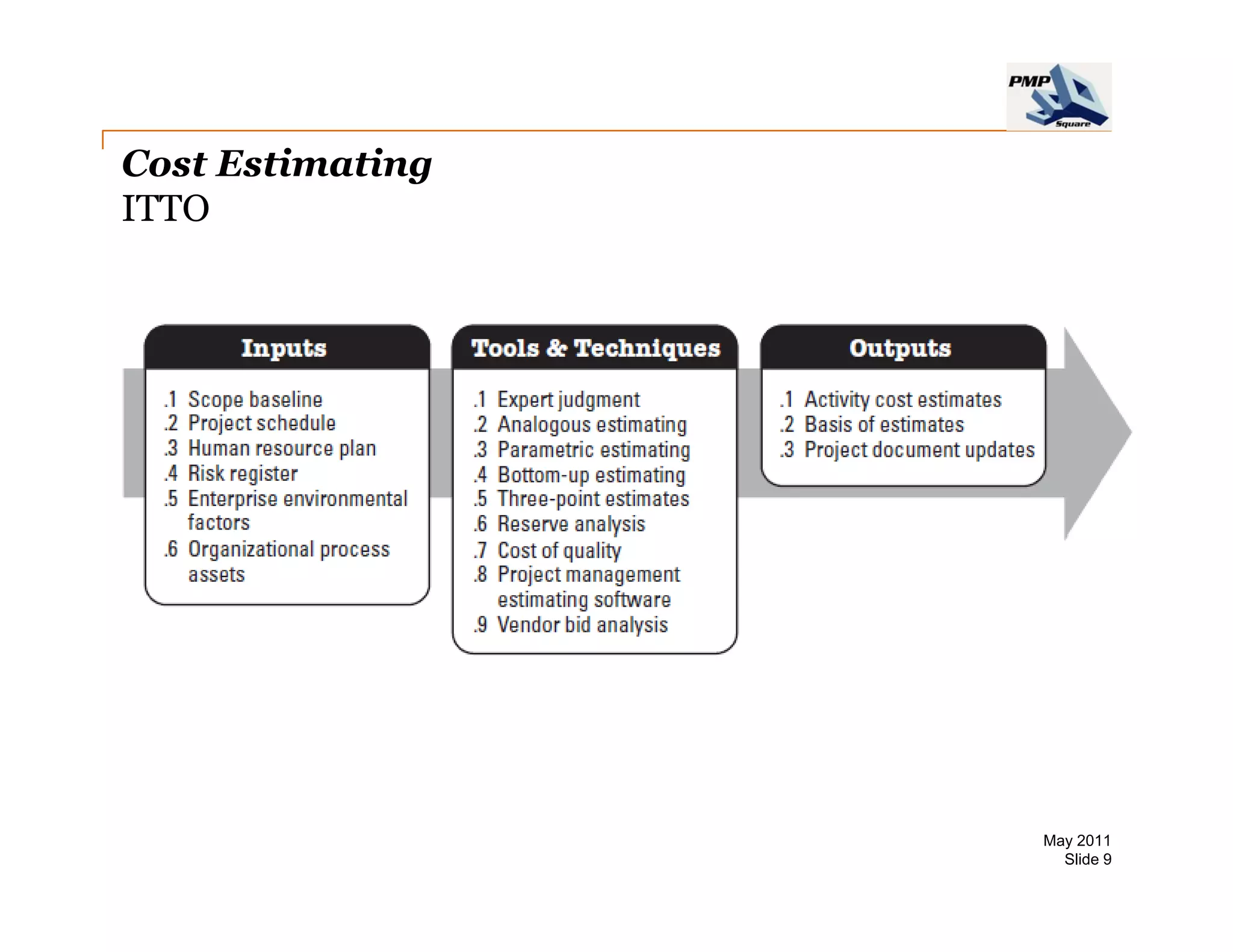
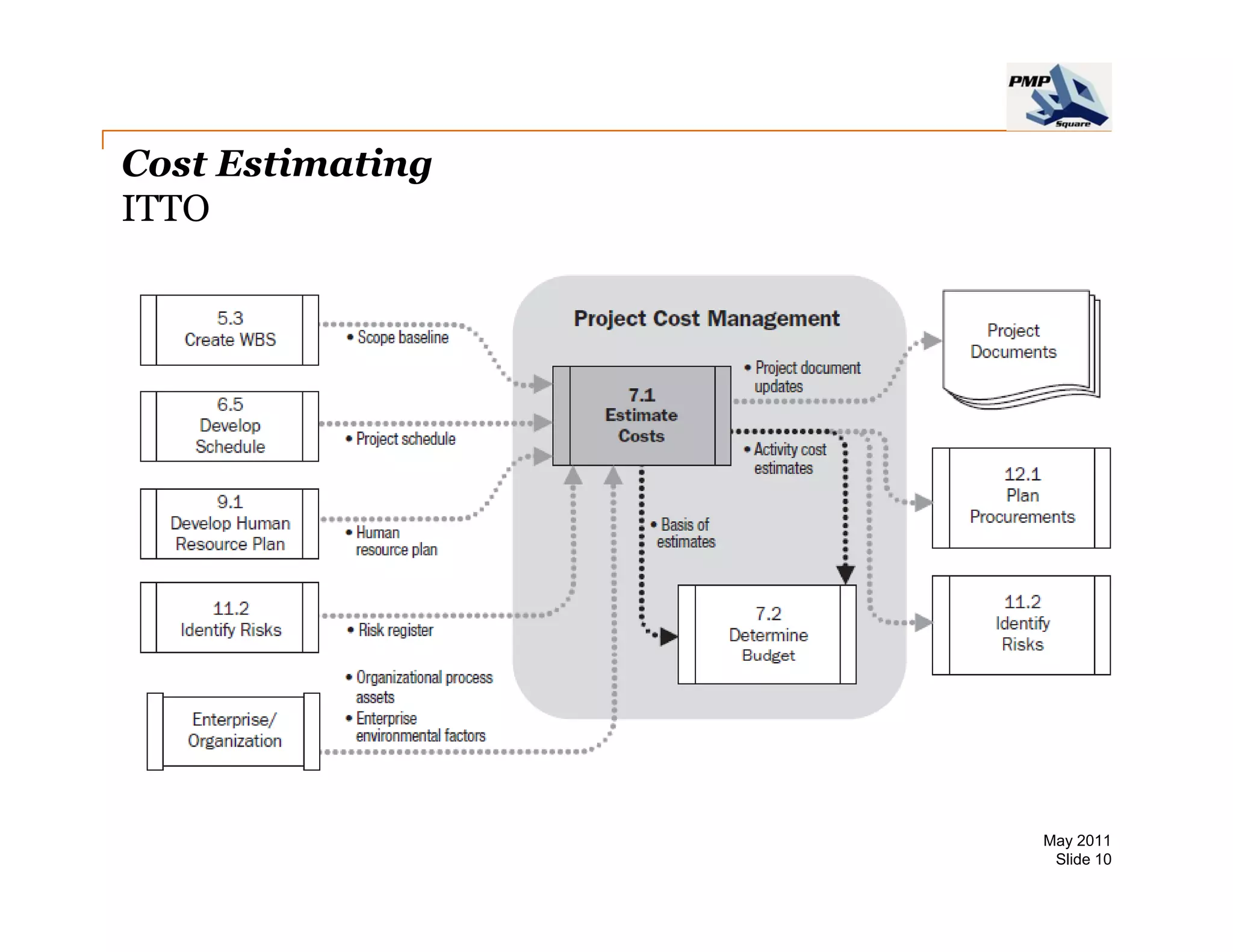
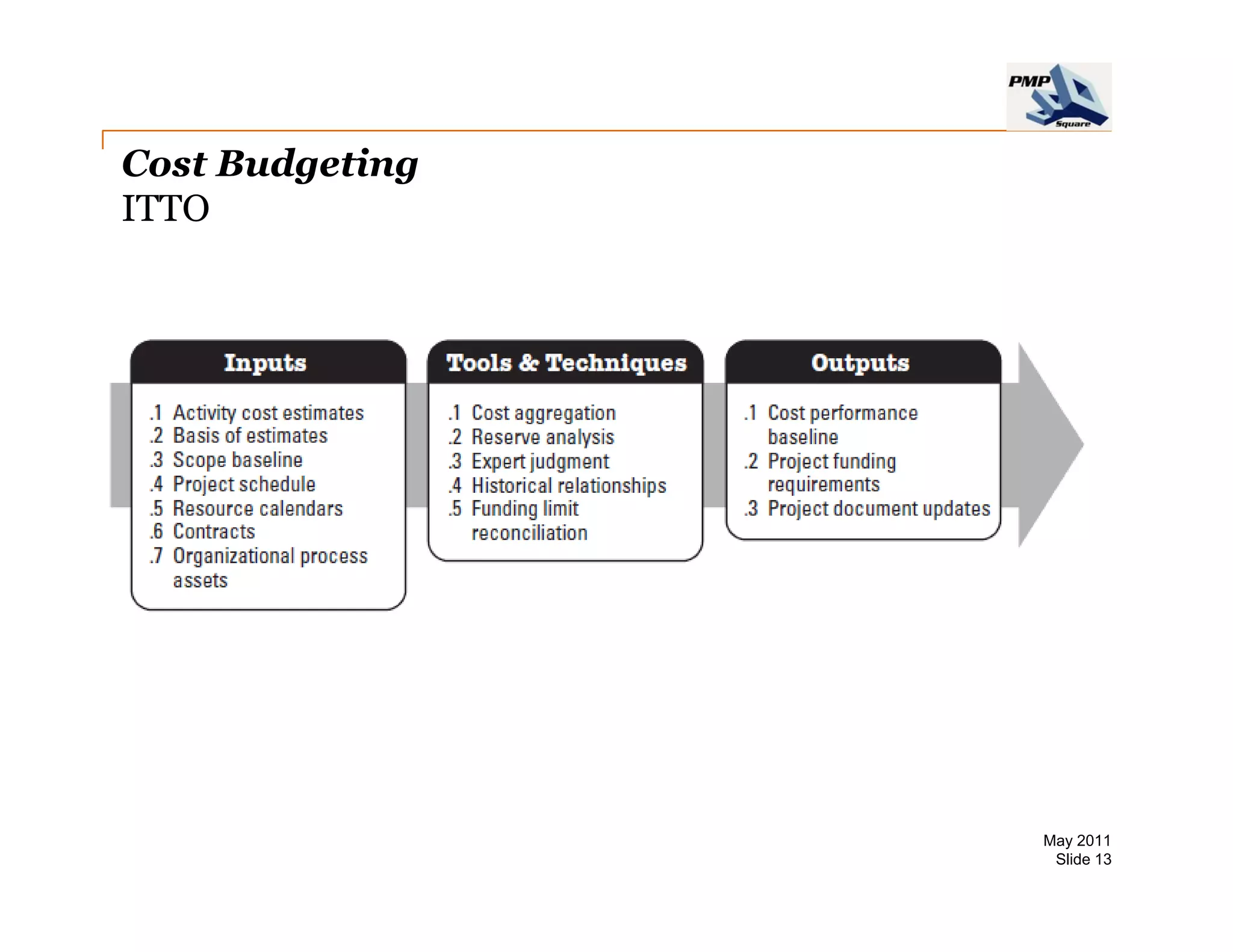
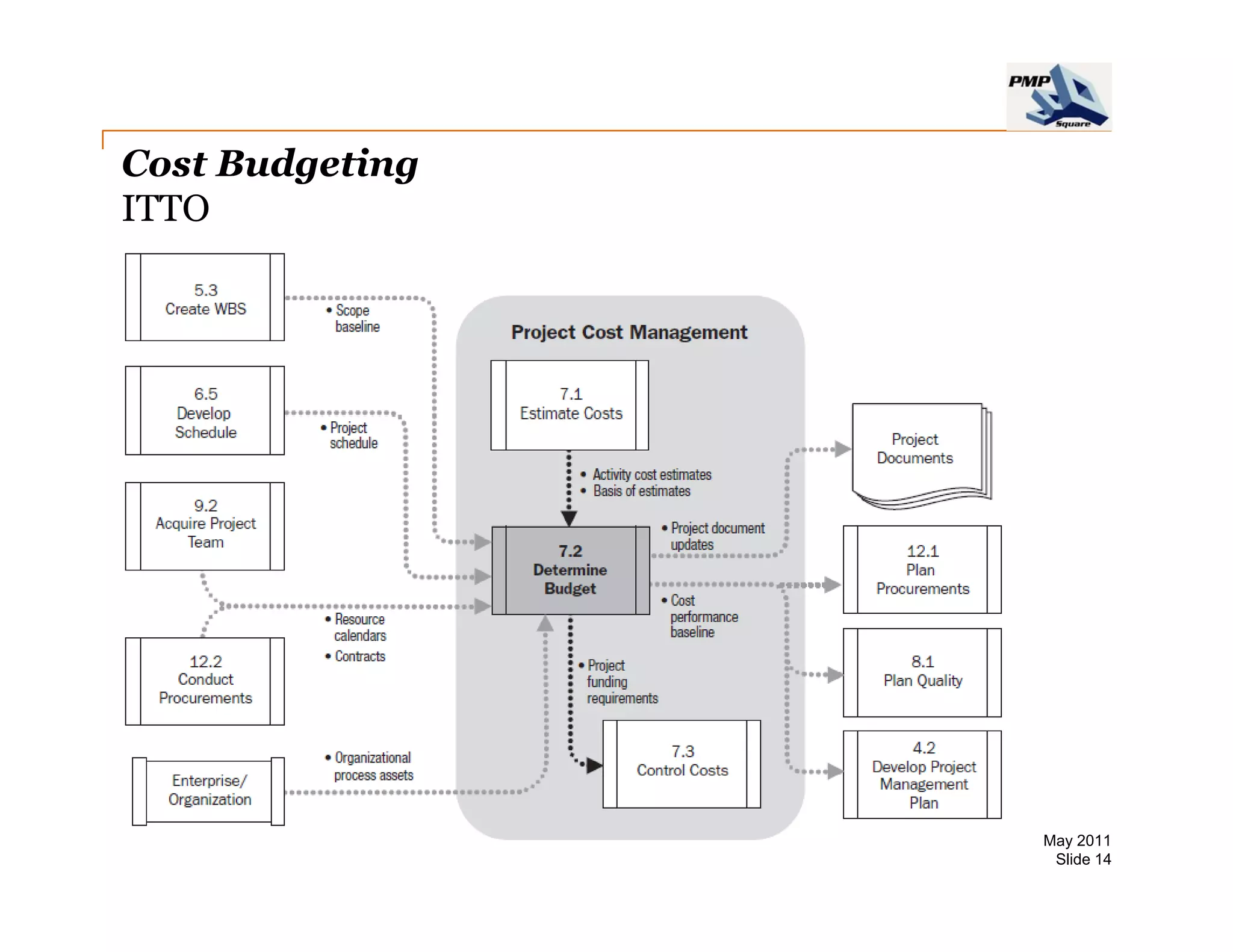
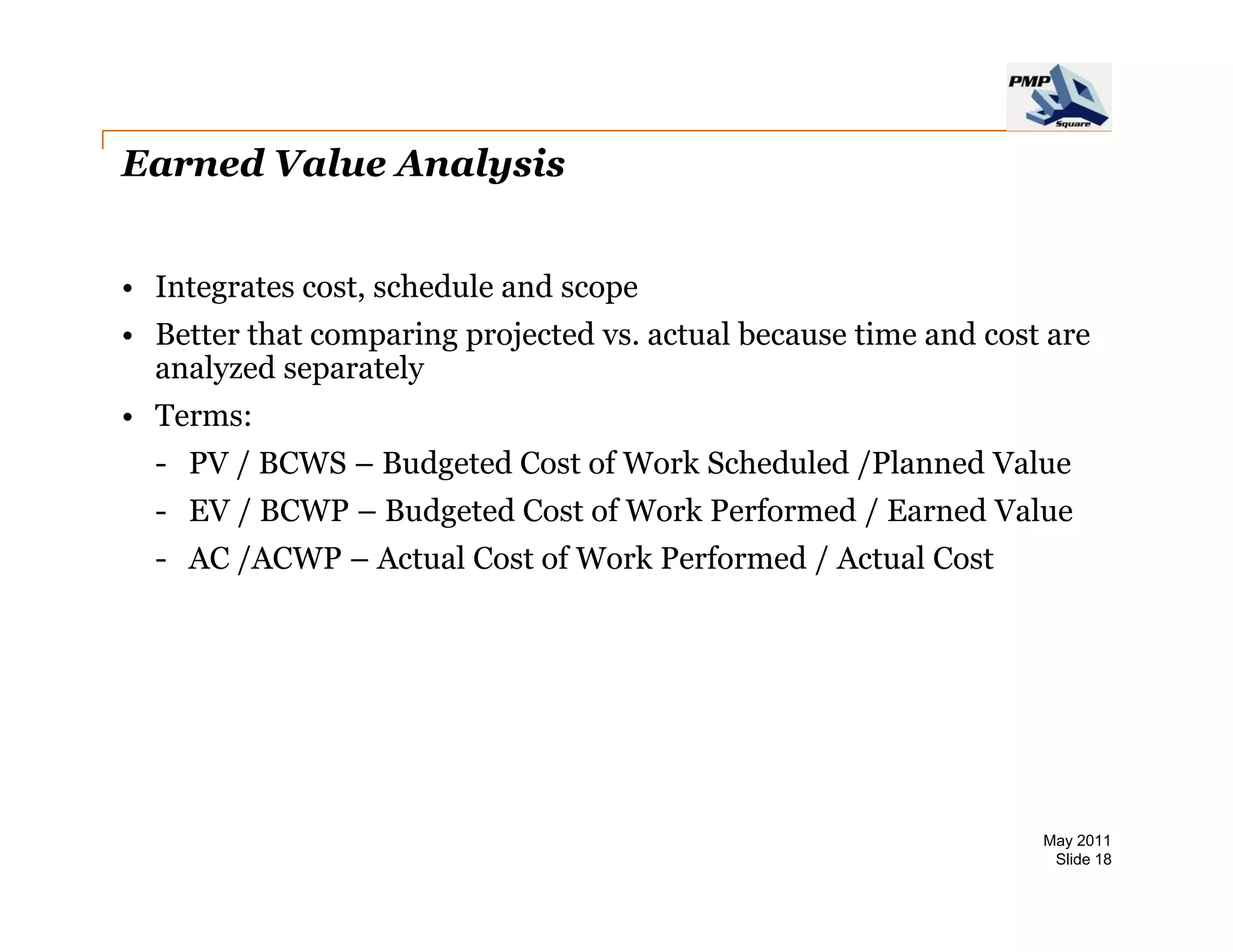
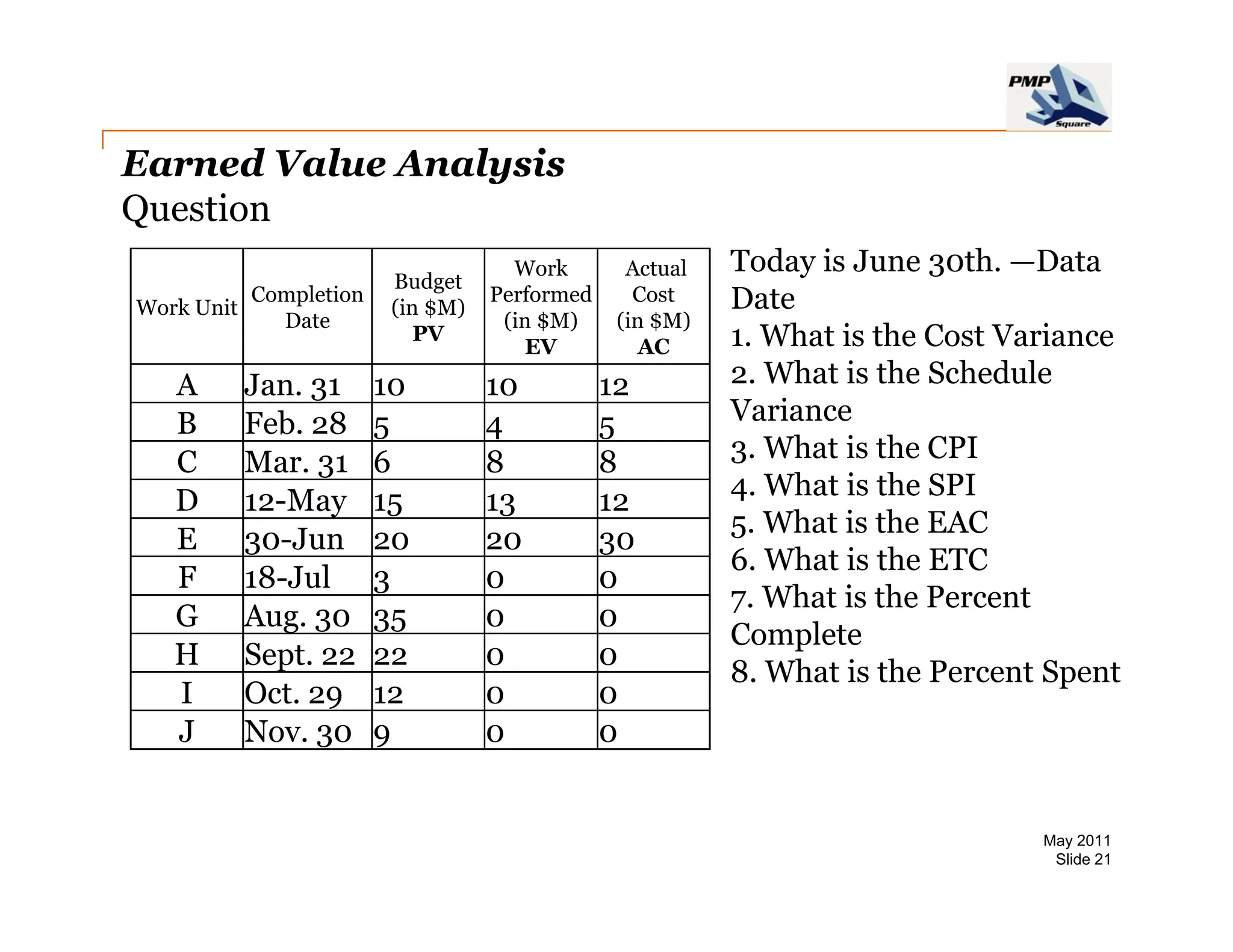
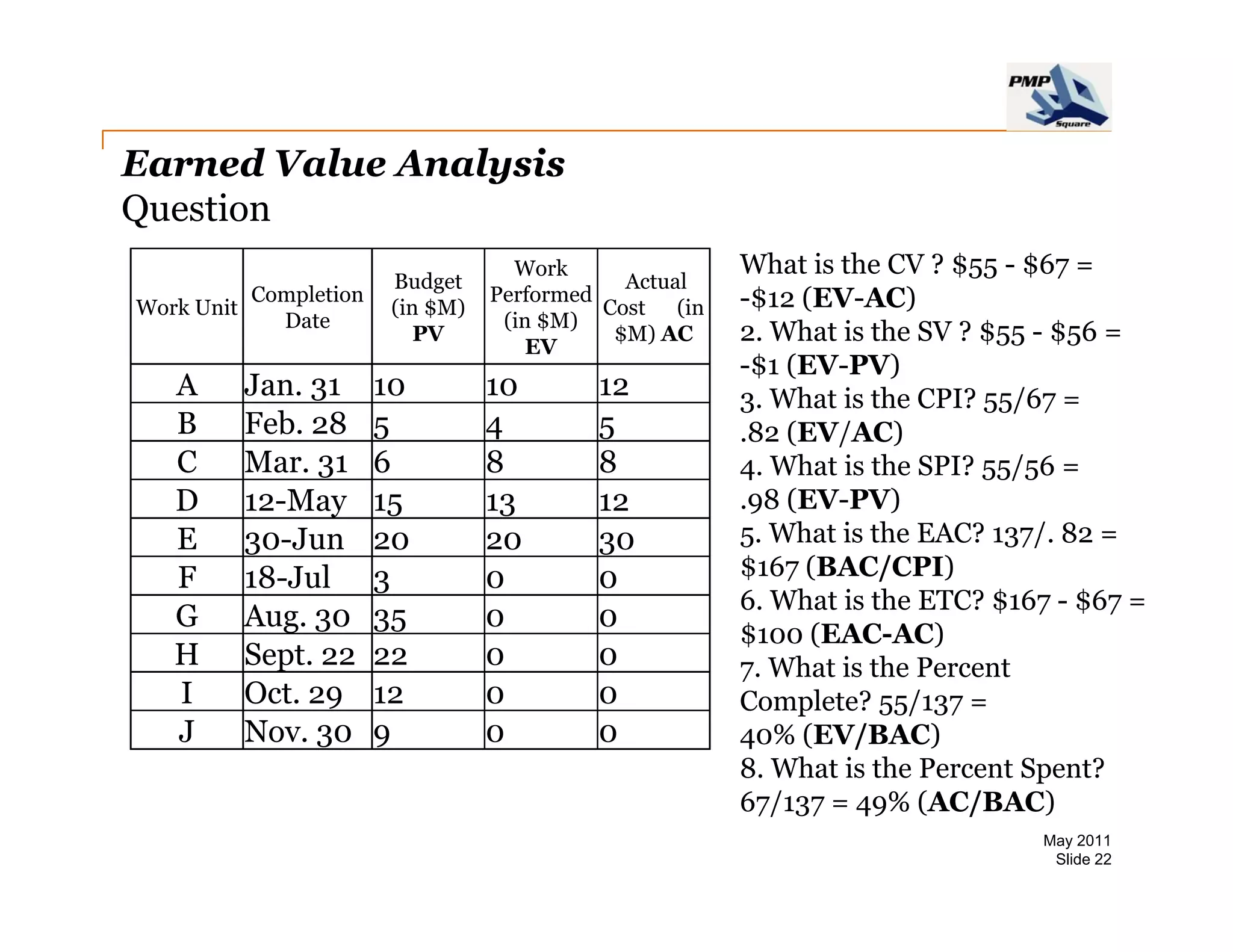
The document provides information on project cost management. It defines cost estimating, budgeting, and control, and describes types of costs like direct, indirect, fixed and variable costs. It also discusses estimation techniques like analogous estimating, parametric estimating, and bottom-up estimating. Cost budgeting involves aggregating estimates to establish a cost baseline. Earned value analysis integrates cost, schedule and scope to analyze performance.