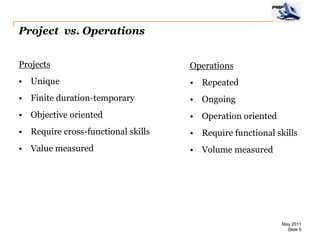
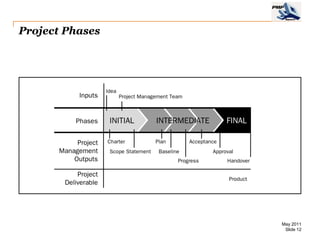
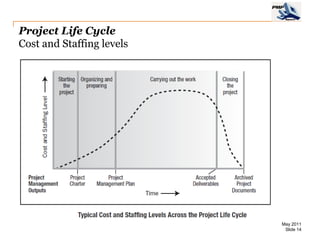
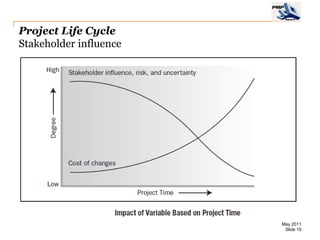
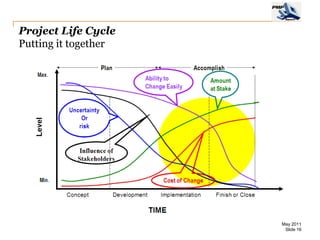
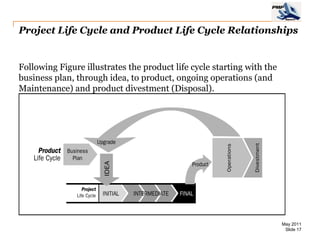
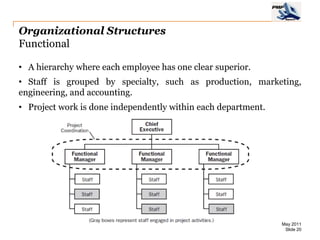
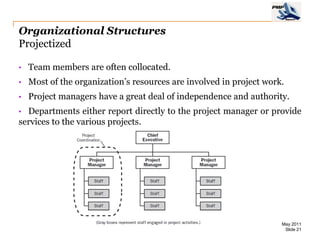
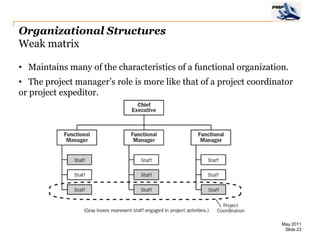
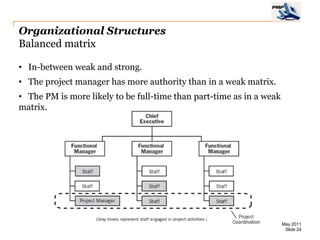
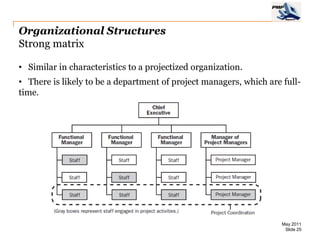
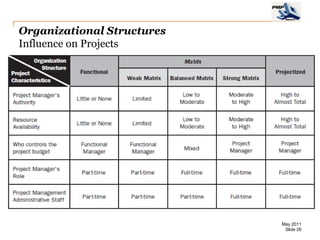
The document provides an overview of project management concepts including business enterprises, projects, programs, operations, the project manager role, project phases and life cycle, stakeholders, and organizational structures. It discusses key definitions such as projects being temporary endeavors to create unique products or results, and programs being groups of related projects. The roles of the project manager and skills needed are outlined. Project phases and typical project life cycles are presented. Stakeholders and different organizational structures like functional, projectized, and matrix are also summarized.