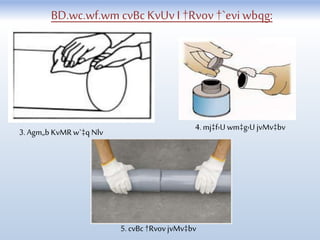
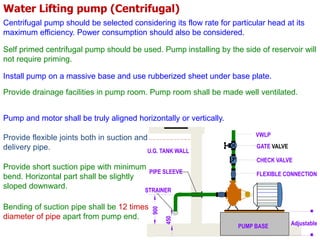
This document provides information on plumbing systems and components. It defines plumbing as the art and science of installing pipes, fixtures, and accessories for water supply, drainage, and ventilation in buildings. It then describes various types of water supply systems, sanitary systems, pipes used in plumbing like uPVC, CPVC, ABS, and galvanized iron pipes. It also discusses valves, traps, fixtures like sinks, water closets, and more. Key points in plumbing installation and various plumbing codes are highlighted.



















































![The pressure is a function of water height and density of water i.e.
P = hD. where h = depth of water in ft and D = density of water
For 1 ft of water column, pressure exerted is
P = h D= [(1 ft) x (62.4) 1b /ft 3)] (1ft2 / 144 in2 ) = 0.433 h psi/ ft depth.
So p = 0.4333 h psi
So one psi pressure is developed for 1/0.433 = 2.304 ft of water column.
h = 2.304 p ft of water column.
Static water pressure
Absolute pressure is the gauge pressure plus 14.7 psi because at mean sea level where the
absolute atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psi. But the gauge reads zero pressure there.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plumbingsystemfortraining22-170208041523/85/Plumbing-system-for-training-22-01-2017-54-320.jpg)























