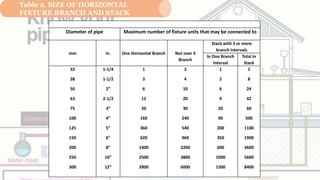
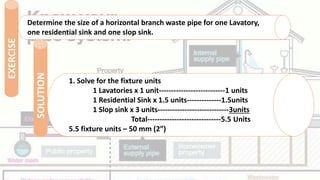
The document discusses waste pipes, their components, materials, installation guidelines, and sizing based on connected fixtures. It provides definitions of waste pipes and explains they receive discharge from fixtures except to the soil branch, soil pipe, or house drain. It describes drainage installation components and classifies stack pipes conveying waste vertically. The document outlines best practices for material selection, fitting use, cleanout placement, pipe slope, joining methods, and proper sizing to ensure effective waste flow. Fixture units are defined based on discharge rates and tables provide maximum connections per pipe diameter. Examples demonstrate calculating pipe sizes for given fixture configurations.