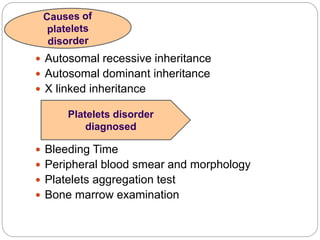
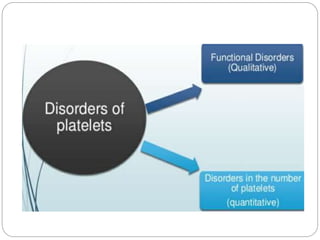
Platelets are a key component of hemostasis, the process of clotting blood after an injury. The document discusses platelets disorders including thrombocytopenia, where platelet counts are too low, and thrombocytosis, where they are too high. Some causes of low or high platelet counts include medications, diseases, infections, and pregnancy. Symptoms of low platelet counts can include bruising, bleeding, and heavy periods. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may involve medications, transfusions, or lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help sustain a normal platelet balance.