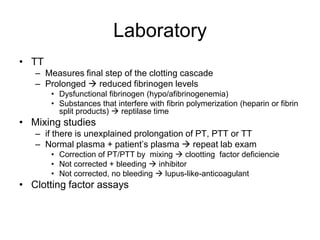
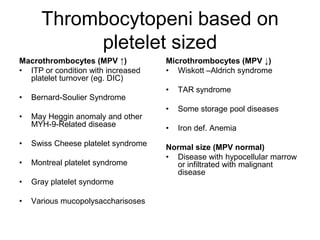
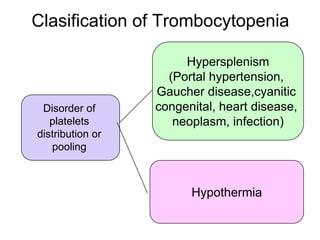
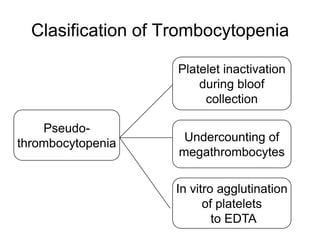
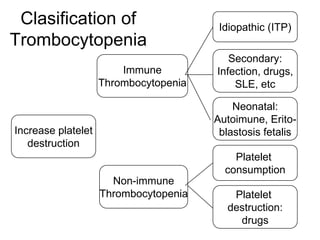
This document discusses hemostasis disease in children, specifically focusing on immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). It describes the mechanisms, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment approaches for ITP. Key points include that ITP is characterized by low platelet count due to increased platelet destruction by autoantibodies, with symptoms of bruising and bleeding. Evaluation involves blood tests to confirm thrombocytopenia and exclude other causes, while treatment may include corticosteroids, IVIG, or splenectomy in severe cases.