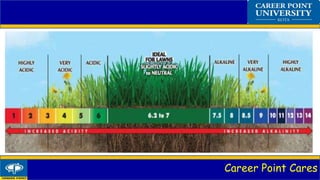
The document discusses three types of problem soils: acidic soils which have a pH below 6.5, alkaline soils which have a pH above 8.5 and a high exchangeable sodium percentage, and saline soils which have an electrical conductivity above 4.0 mmhos/cm. It describes the characteristics, impacts on crop growth, suitable crop varieties and amelioration methods for each type of problem soil. The amelioration methods aim to raise pH, leach excess salts, or replace exchangeable sodium to make the soils more suitable for crop cultivation.