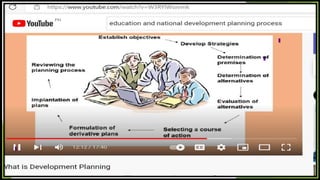
Planning is an essential managerial process that involves setting goals and determining how to achieve them. The planning process consists of 7 steps: (1) setting objectives, (2) developing planning premises, (3) identifying alternative courses of action, (4) evaluating alternatives, (5) selecting the best alternative, (6) implementing the plan, and (7) follow up. Effective planning requires managers to carefully consider objectives, assumptions, options, impacts, and feedback to develop and execute strategies for achieving organizational goals.