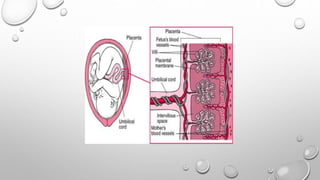
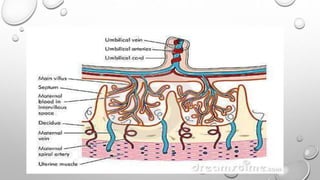
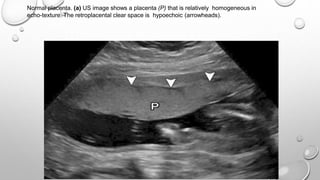
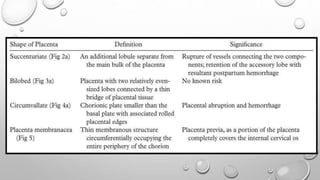
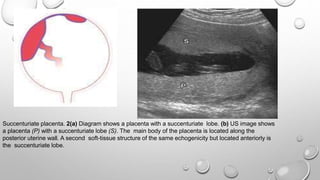
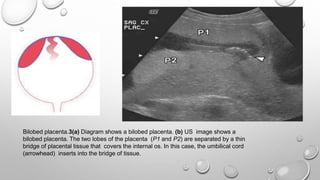
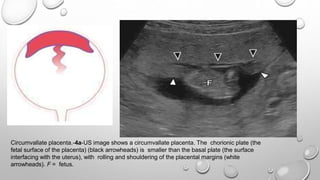
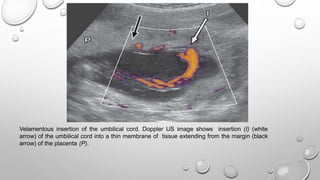
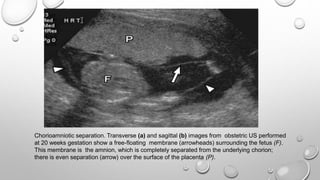
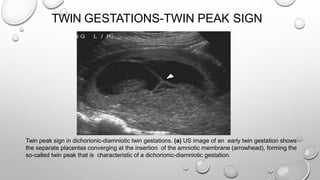
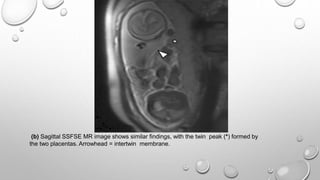
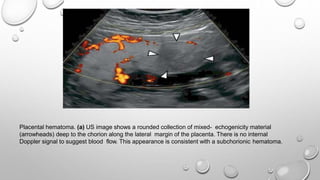
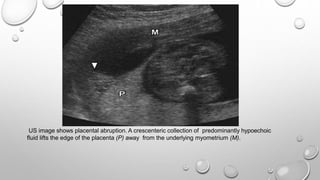
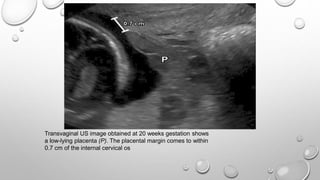
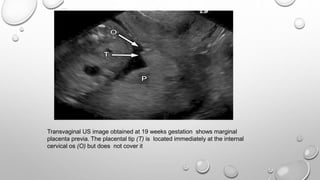
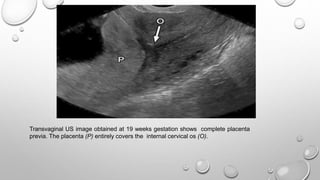
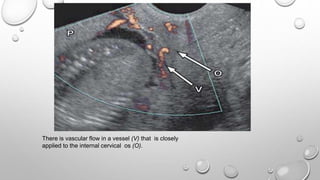
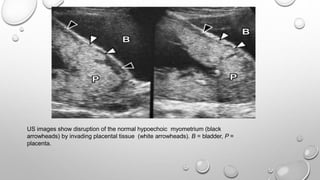
The document discusses the importance of imaging the placenta due to potential maternal and fetal morbidity related to its abnormalities. It covers various conditions such as placenta previa, accreta, and placental tumors, as well as imaging techniques like sonography and MRI for evaluation. Emphasizing the role of proper diagnosis, it details different placental morphologies and their implications during gestation.