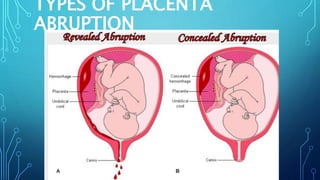
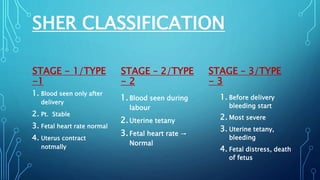
Placental abruption, a premature separation of a normally implanted placenta, can be life-threatening for both the mother and baby, with serious complications including shock, organ failure, restricted growth, and premature birth. The document outlines various causes and types, stages, clinical presentation, and management strategies for different scenarios of placental abruption. Diagnosis involves monitoring fetal heart rates, ultrasound, and laboratory tests, while treatment varies based on the timing and condition of both mother and fetus.