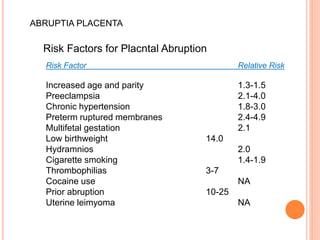
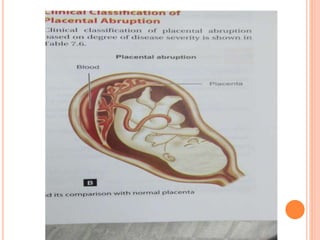
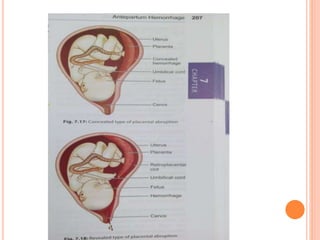
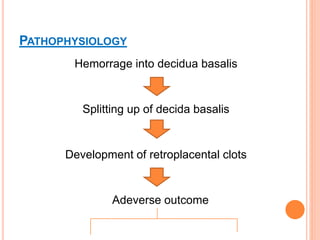
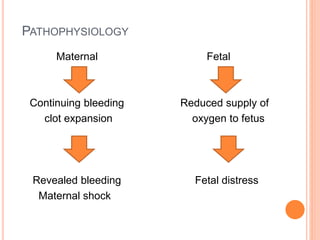
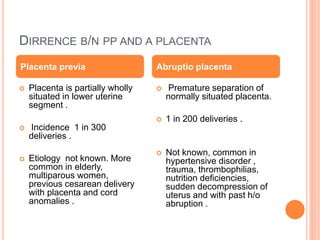
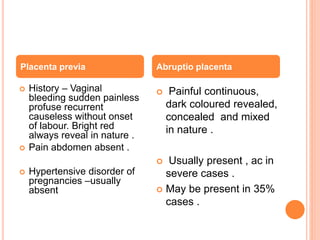
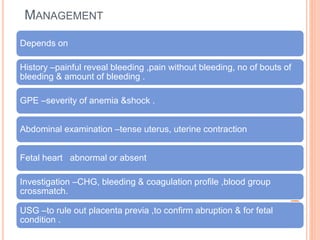
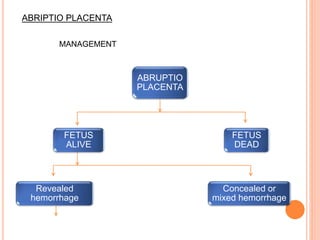
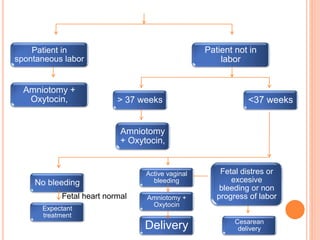
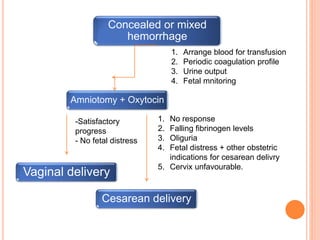
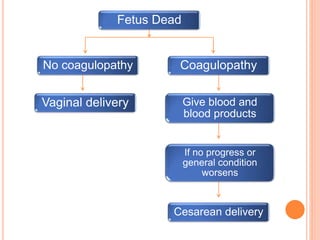
Abruptio placenta is the premature separation of a normally positioned placenta from the uterus, occurring in about 1 in 200 pregnancies. Major risk factors include advanced maternal age, high parity, hypertensive disorders, and trauma, with clinical presentations ranging from subtle to severe, often including dark red vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. Management varies from observation in stable cases to urgent delivery in severe cases, and complications can impact both maternal and fetal health significantly.