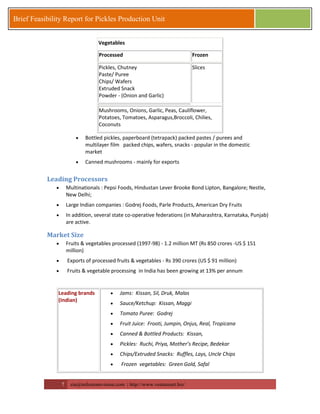
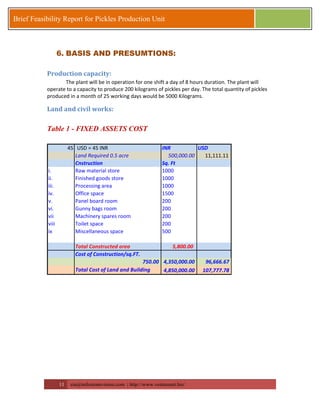
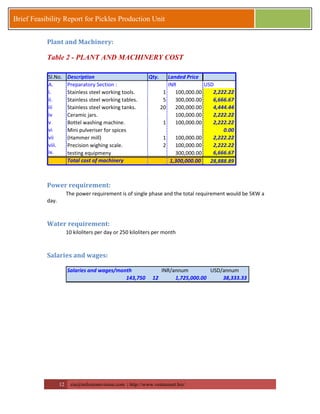
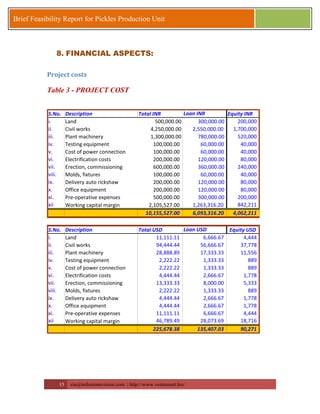
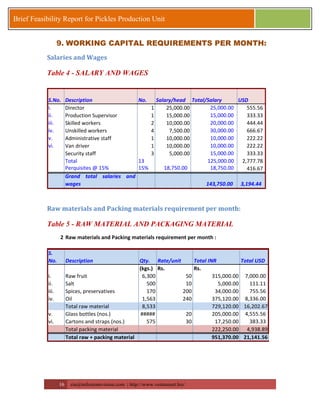
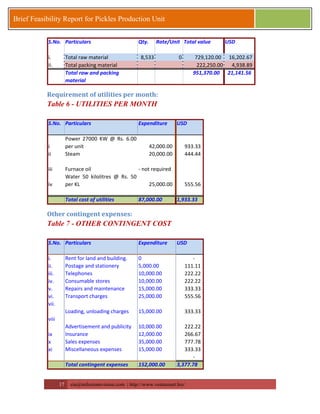
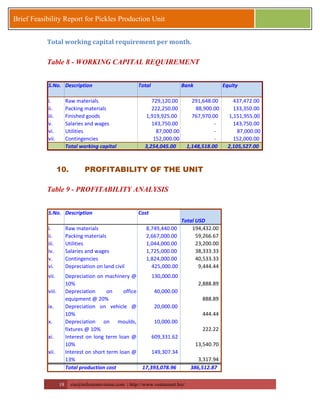
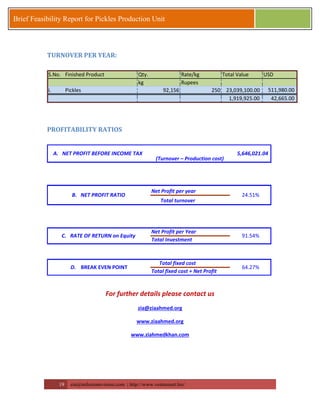
This document provides a brief feasibility report on starting a pickles production unit. It discusses the history and production methods of pickles, as well as the Indian market for processed fruits and vegetables including production capacities, leading processors, market size, exports, and key success factors. Pickles are one of the oldest processed foods and an important food preservation method. Small and micro enterprises can start small pickles production units depending on needs.