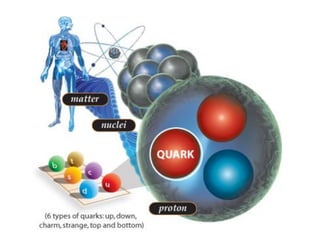
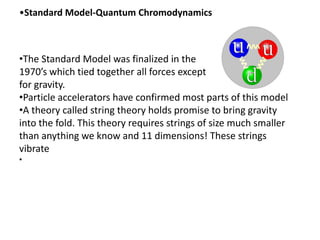
This document provides information about an introductory physics course, including contact information for the instructor and a link to the course website. It then summarizes key topics and developments in the history of physics, from ancient Greek philosophers to modern quantum mechanics and string theory. Major figures discussed include Galileo, Newton, Maxwell, Einstein, Bohr, Feynman, and Gell-Mann. The document traces the development of theories like classical mechanics, electromagnetism, relativity, quantum mechanics, and the Standard Model.