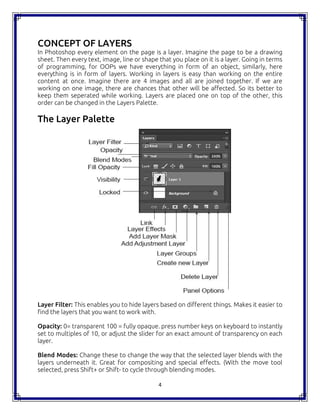
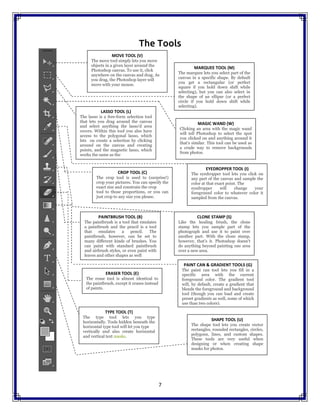
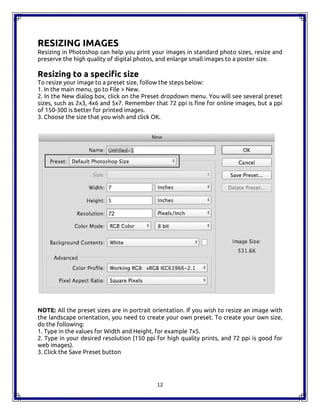
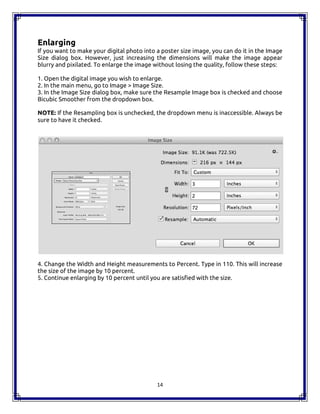
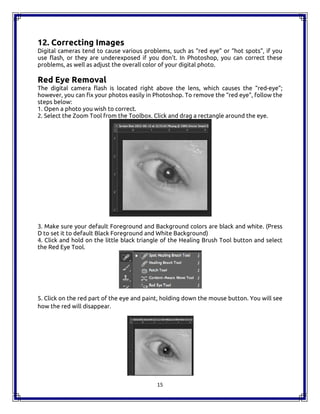
The document is a comprehensive handbook on Adobe Photoshop CC 2015, outlining its features, tools, and functionalities. It covers fundamental concepts such as layers, image correction, and essential shortcuts, while also comparing Photoshop to open source alternatives like GIMP. Each tool and layer functionality is explained, providing users with valuable insights for effective usage of the software.