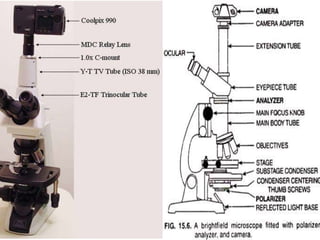
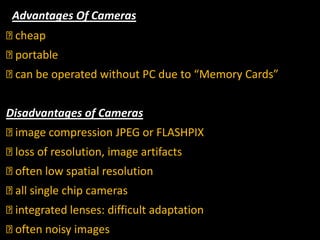
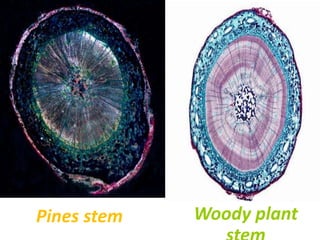
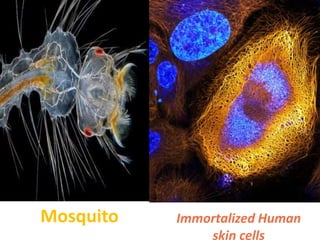
This document discusses photomicrography, which is the process of capturing microscope images using cameras. It notes that Thomas Wedgwood first proposed the idea of photomicrography in 1771. A photomicrograph provides a technical or beautiful image that can benefit science or industry by studying the external structure of objects. Various cameras and light sources can be used for photomicrography. Applications of photomicrography include medical research, ecology, agriculture, criminal investigations, and education.