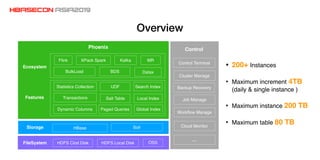
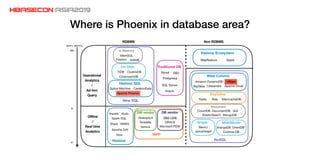
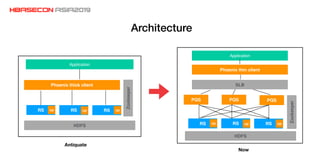
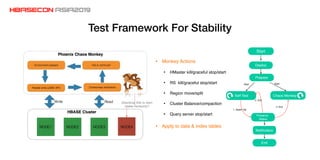
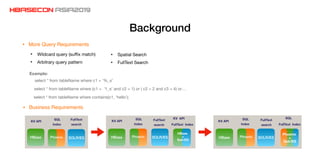
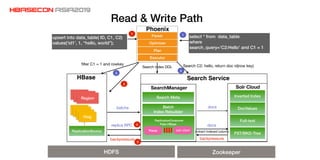
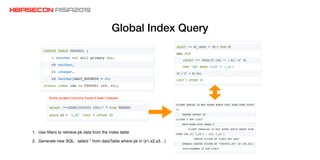
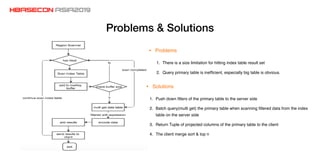
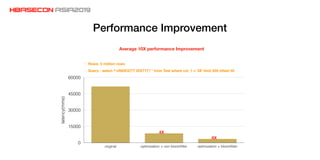
The document discusses advancements and practices for Apache HBase and Phoenix on Alibaba Cloud, covering topics such as performance improvements, ecosystem tools, data migration, and client architecture. It emphasizes benefits like high throughput, low latency query execution, and strategies for indexing and data management. Additionally, it outlines best practices, pitfalls to avoid, and future work directions in enhancing search index capabilities and query performance.