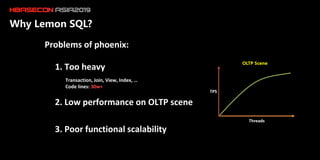
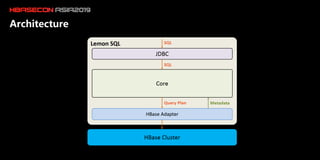
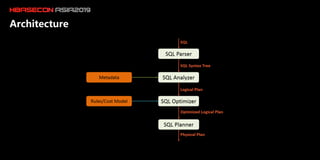
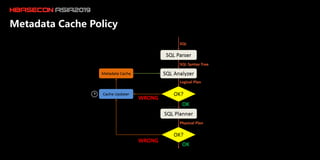
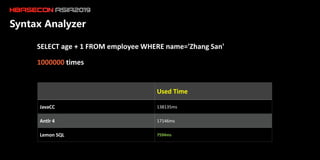
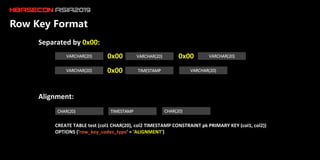
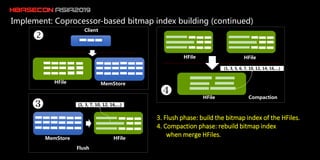
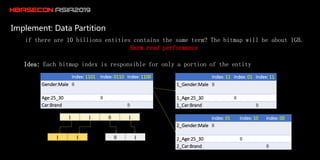
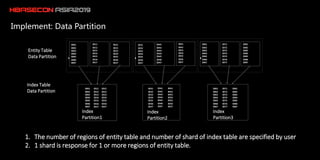
The document discusses the limitations of HBase in handling ad-hoc queries for large datasets with multiple tags and introduces a distributed bitmap index solution to address these challenges. It outlines the architecture for a new SQL engine, Lemon SQL, that enables efficient high-performance querying and better memory management for high-dimensional data. The proposed framework includes coprocessor-based bitmap index building and querying, aimed at enhancing data access and scalability for applications requiring complex search functionalities.





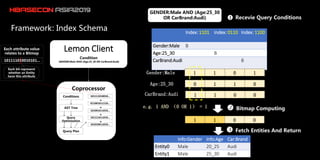




![Query grammar in BNF:
Query ::= ( Clause )+
Clause ::= ["AND", "OR", "NOT"] ([Field:]Value | "(" Query ")" )
• A Query is a series of clauses. Each Clause can also be a nested query
• Supports AND/OR/NOT operators. AND indicates this clause is required, NOT
indicates this clause is prohibited, OR indicates this clause should appear in the
matching results. The default operator is OR is none operator specified.
• Parenthese “(”“)”can be used to improve the priority of a sub-query
- Query: Query Grammar
API
- Put: Write interfaces are the same as hbase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6hbaseconasia2019track11530-190819220932/85/hbaseconasia2019-Distributed-Bitmap-Index-Solution-19-320.jpg)