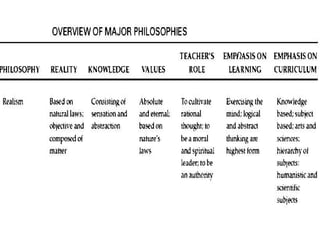
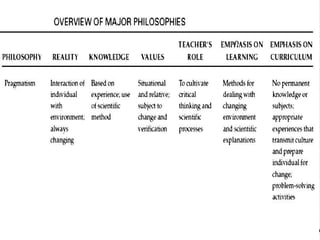
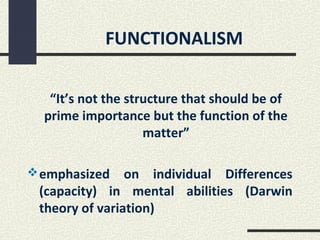
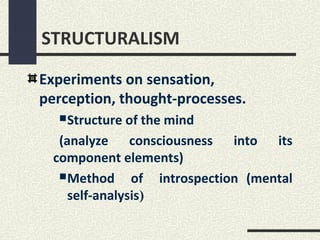
The document discusses several philosophies that influence education, including idealism, behaviorism, socialism, functionalism, purposivism, structuralism, associationism, and utilitarianism. It explains that a school's philosophy guides its goals and curriculum organization. Philosophies like behaviorism focus on modifying student behavior through stimuli and response, while socialism views students as social creatures who help transmit cultural values to society.