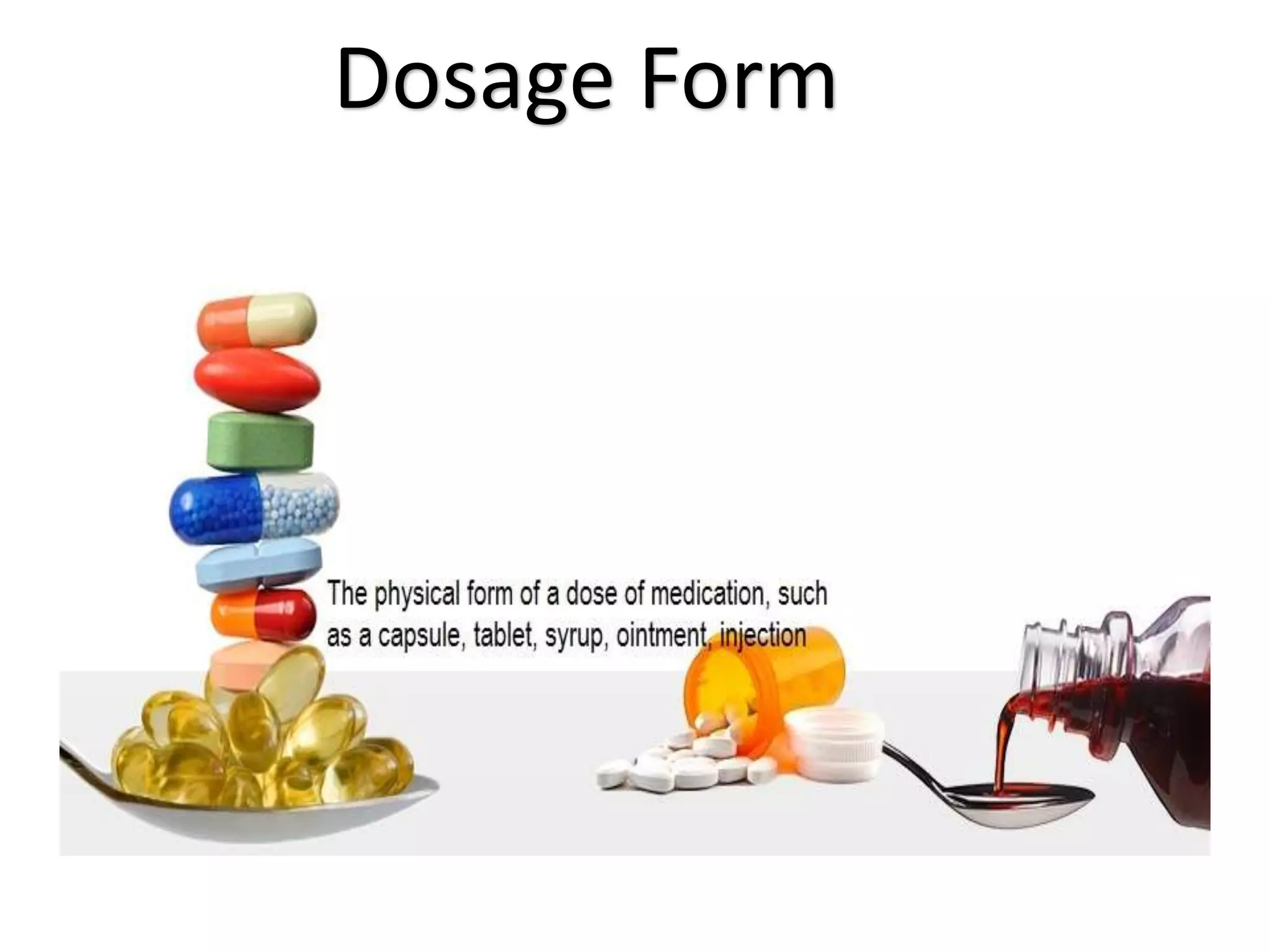
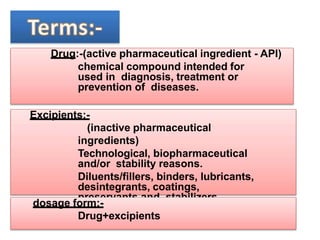
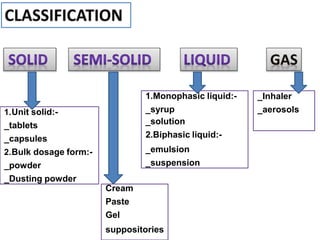
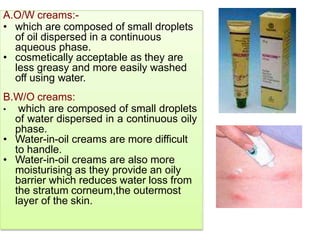
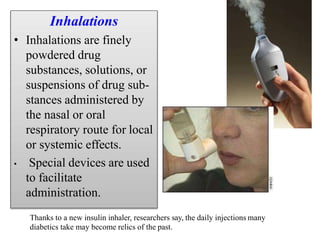
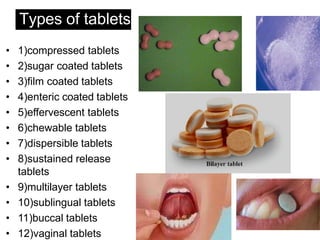
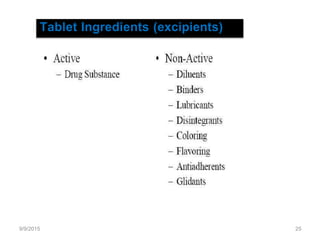
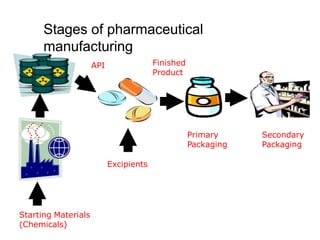
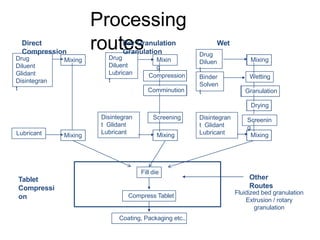
This document discusses various dosage forms used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It describes dosage forms as drug formulations containing active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients that are used for diagnosis, treatment or prevention of diseases. Some key dosage forms mentioned include tablets, capsules, powders, liquids, semisolids, creams, ointments, inhalers, suppositories and aerosols. Tablets and capsules are described as the most common unit solid dosage forms. The document also provides details on the composition, manufacturing process and common types of tablets.