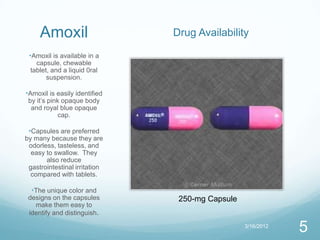
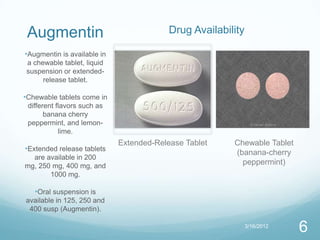
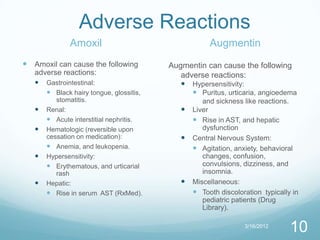
Amoxil vs. Augmentin compares the antibiotics amoxicillin and amoxicillin/clavulanate. Amoxil contains only amoxicillin, which stops bacterial cell wall synthesis. Augmentin combines amoxicillin with clavulanate, which stops bacterial beta-lactamase. Augmentin is more expensive and has more side effects than Amoxil. Both antibiotics are well absorbed, partially metabolized in the liver, and mainly excreted in urine.