The document discusses the structure and composition of Earth's atmosphere. It can be summarized as follows:
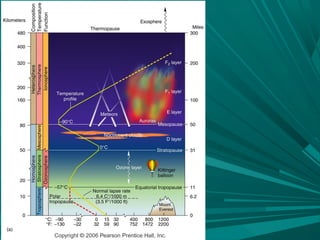
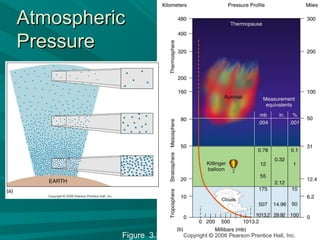
1) The atmosphere extends up to 32,000 km from Earth's surface and is composed primarily of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
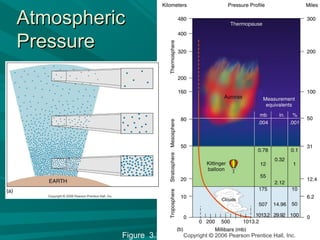
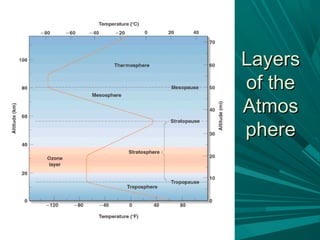
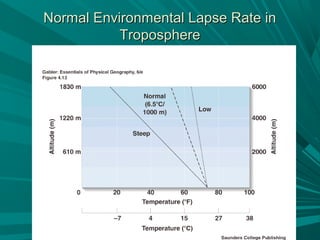
2) Temperature and pressure vary with altitude, with the troposphere being the lowest layer where weather occurs and temperatures generally decrease with height.
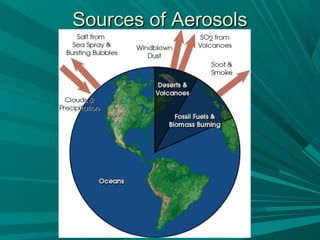
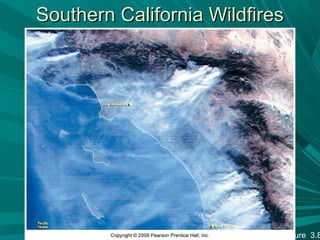
3) The atmosphere contains variable components like pollutants, aerosols from both natural and human-made sources, and water vapor that influence climate and air quality.