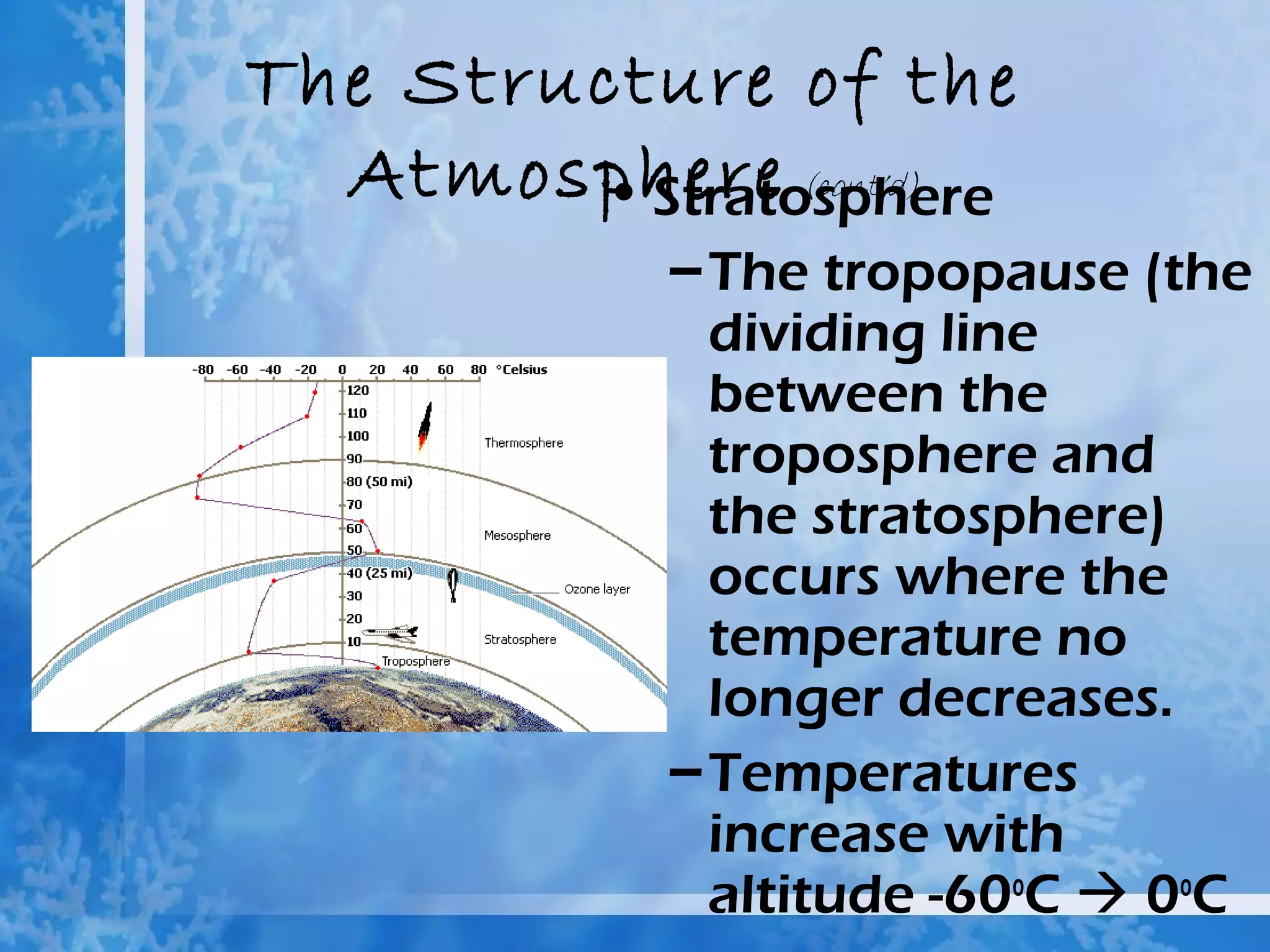
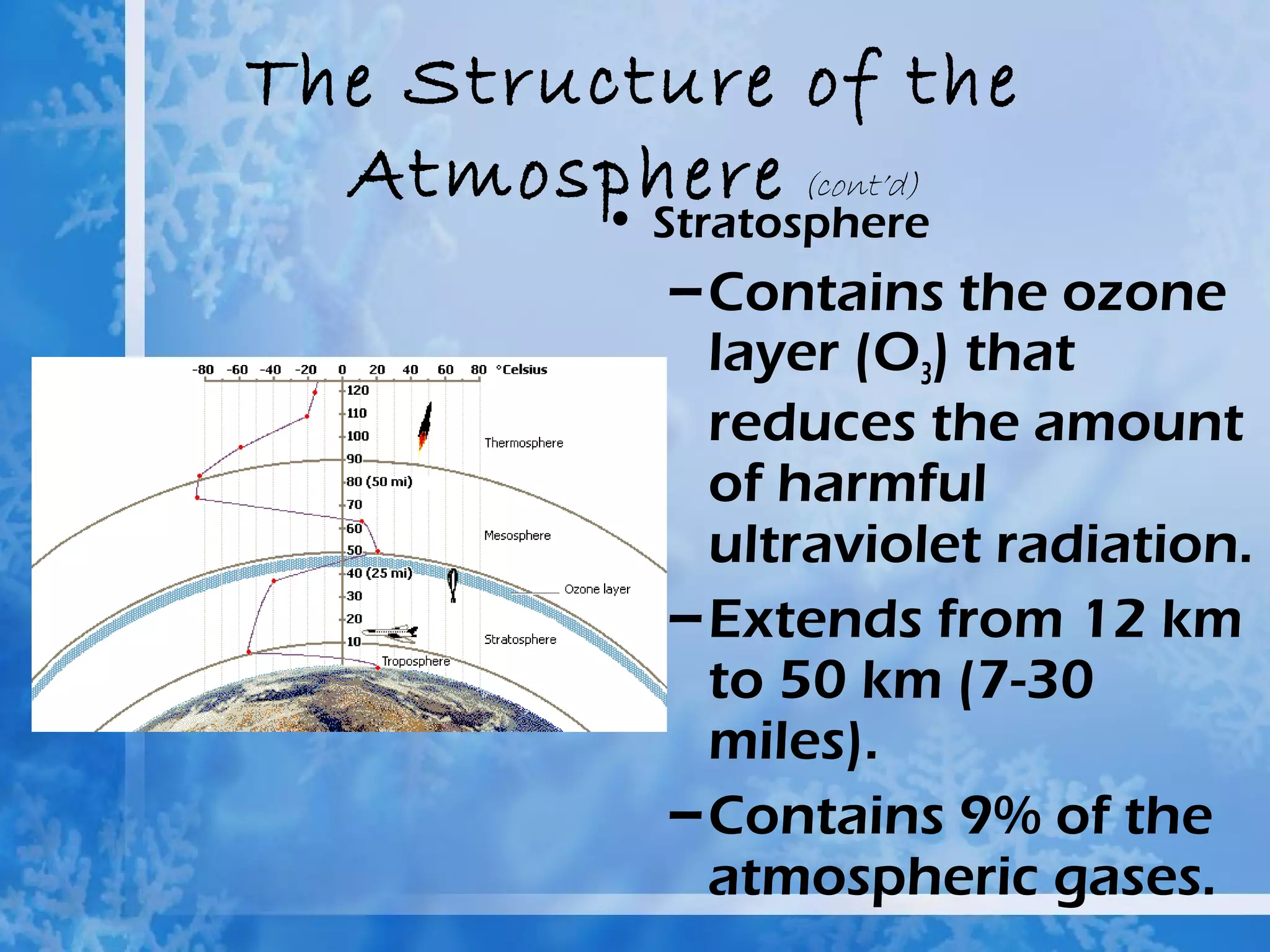
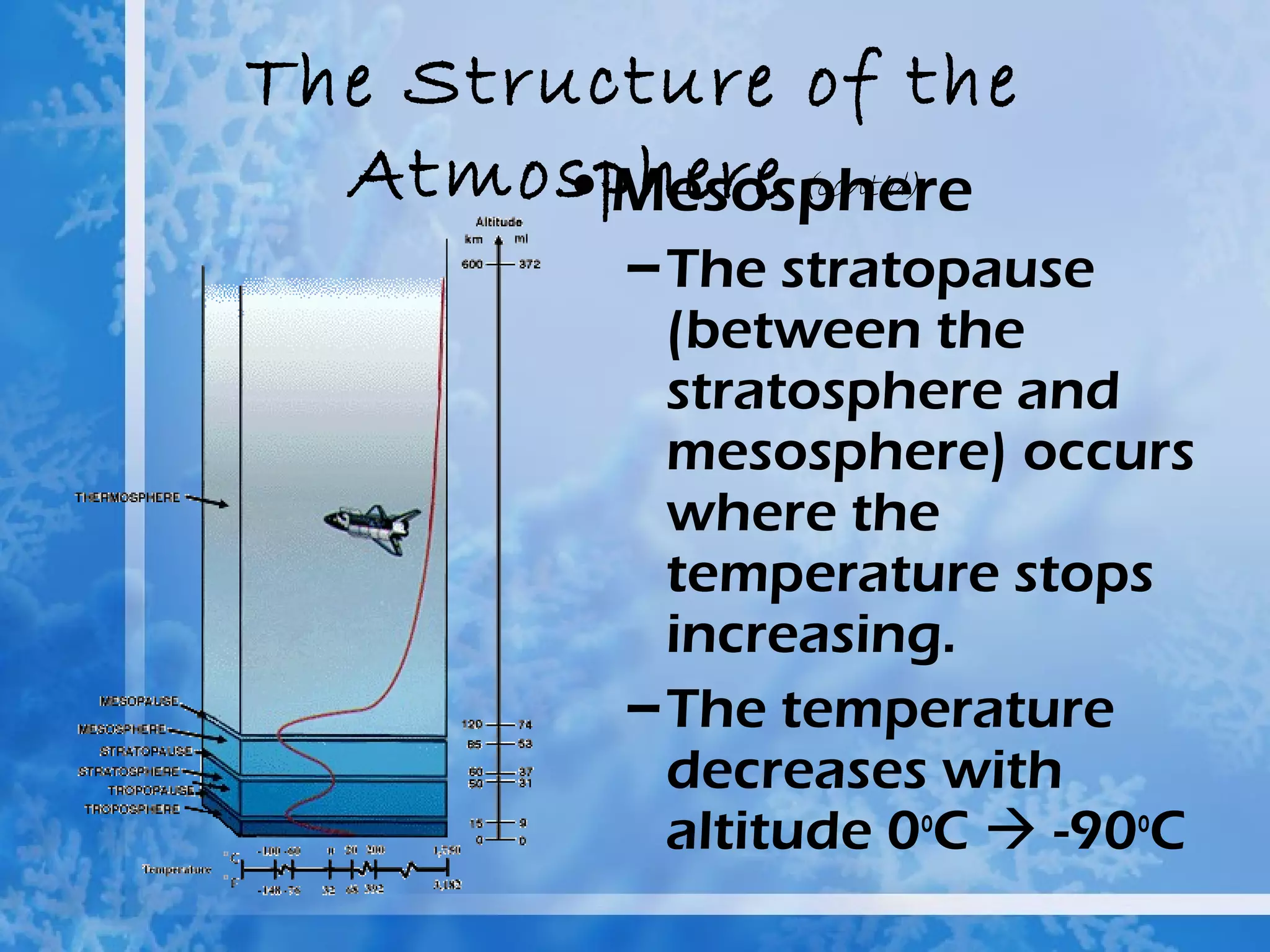
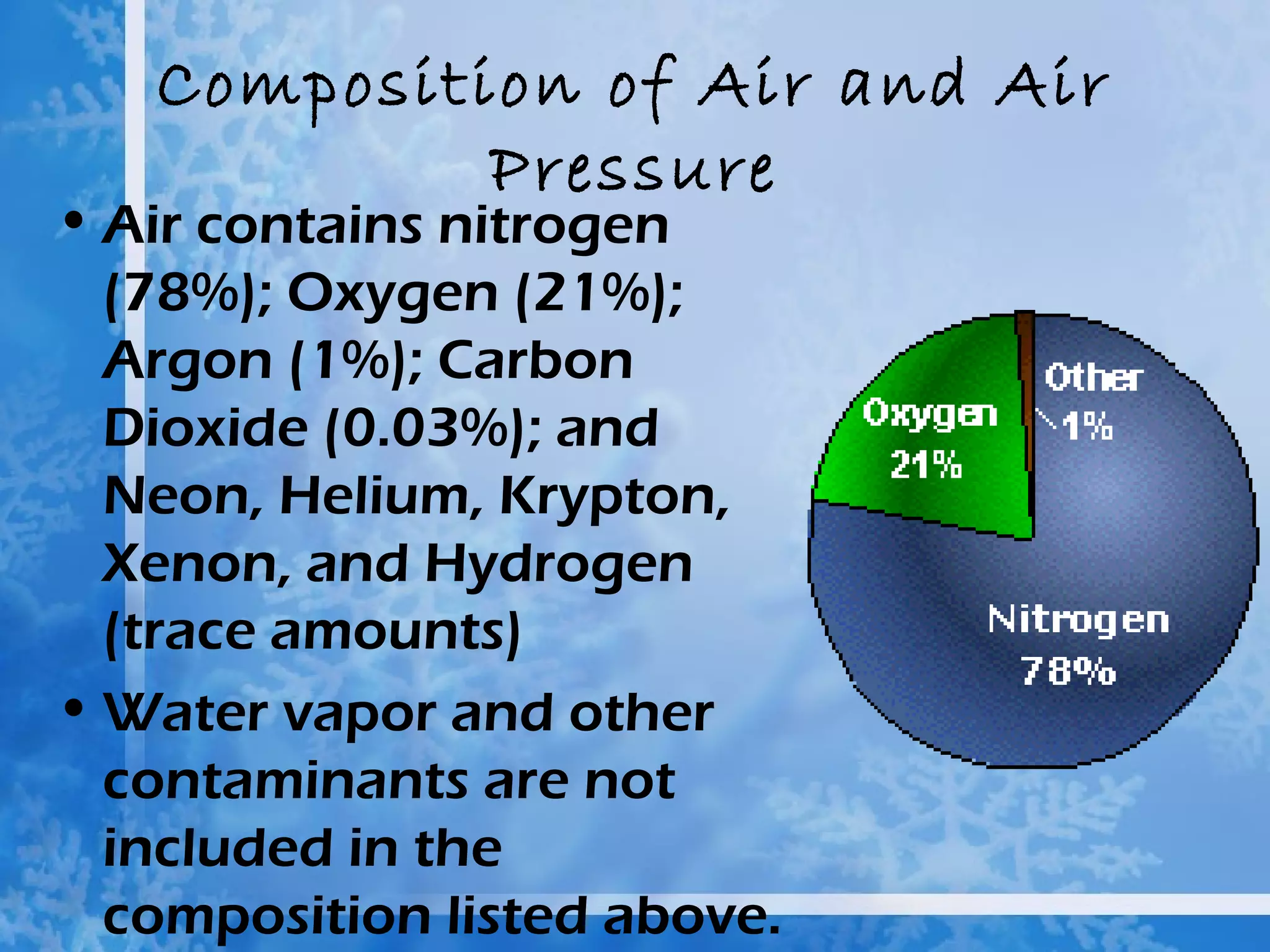
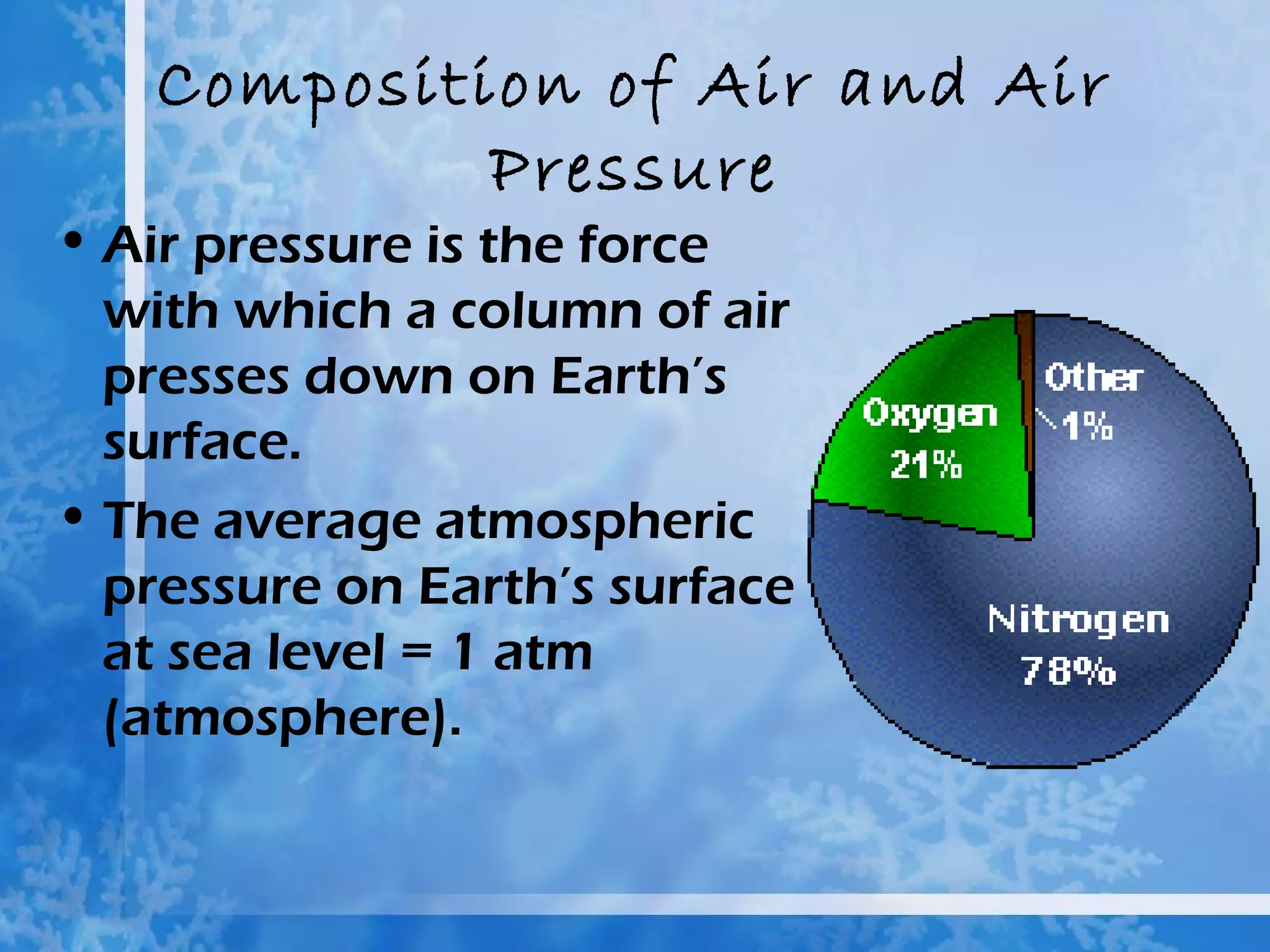
The atmosphere is divided into four main layers - the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. Each layer is defined by changes in temperature. The troposphere extends from Earth's surface to around 12 km and contains around 90% of the atmosphere. The stratosphere extends from 12-50 km and contains the ozone layer which absorbs harmful UV radiation. Air is composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%).