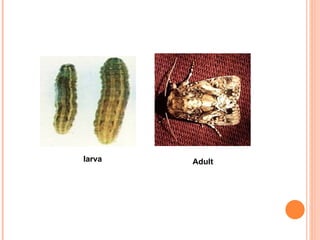
This document provides information on various pests that affect rice crops, including their names, descriptions of damage symptoms, and recommendations for management. It discusses pests such as rice thrips, rice grasshopper, rice gundhi bug, armyworm, rice caseworm, rice hispa, rice leaf folder, brown plant hopper, green plant hopper, white backed plant hopper, rice stem borer, and Asian gall midge. For each pest, it provides details on cultural, biological and chemical control methods that can be used for management.