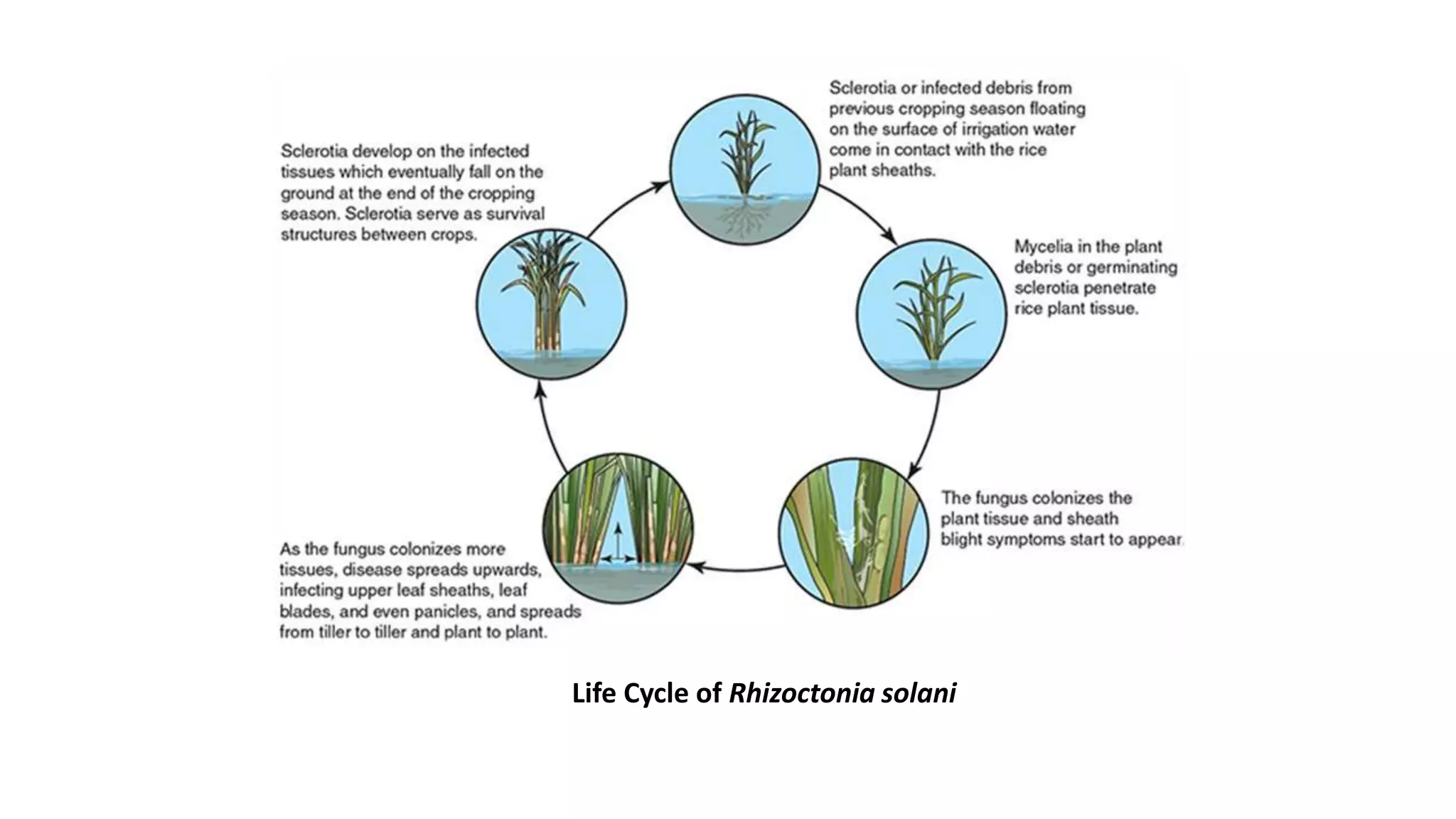
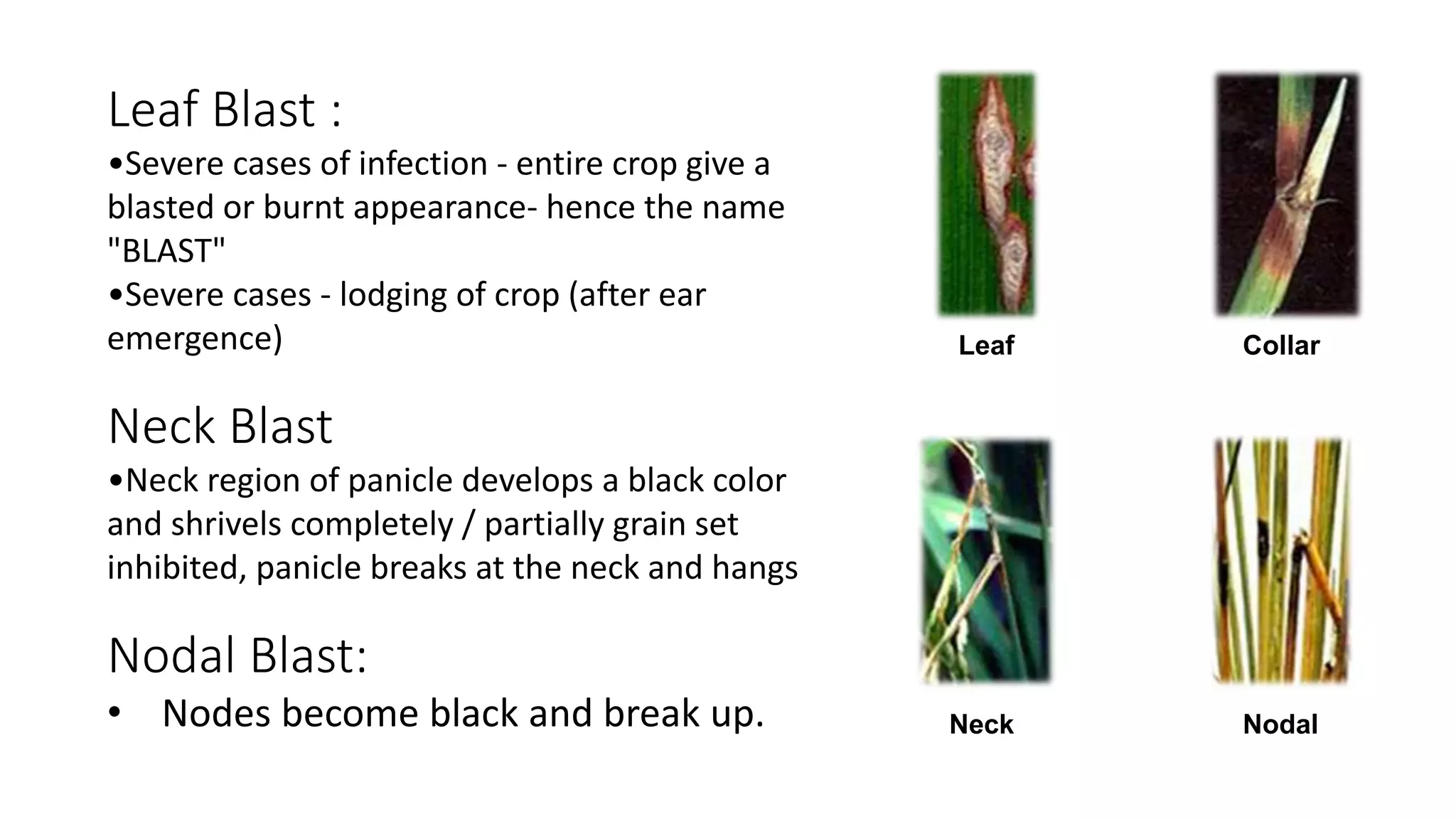
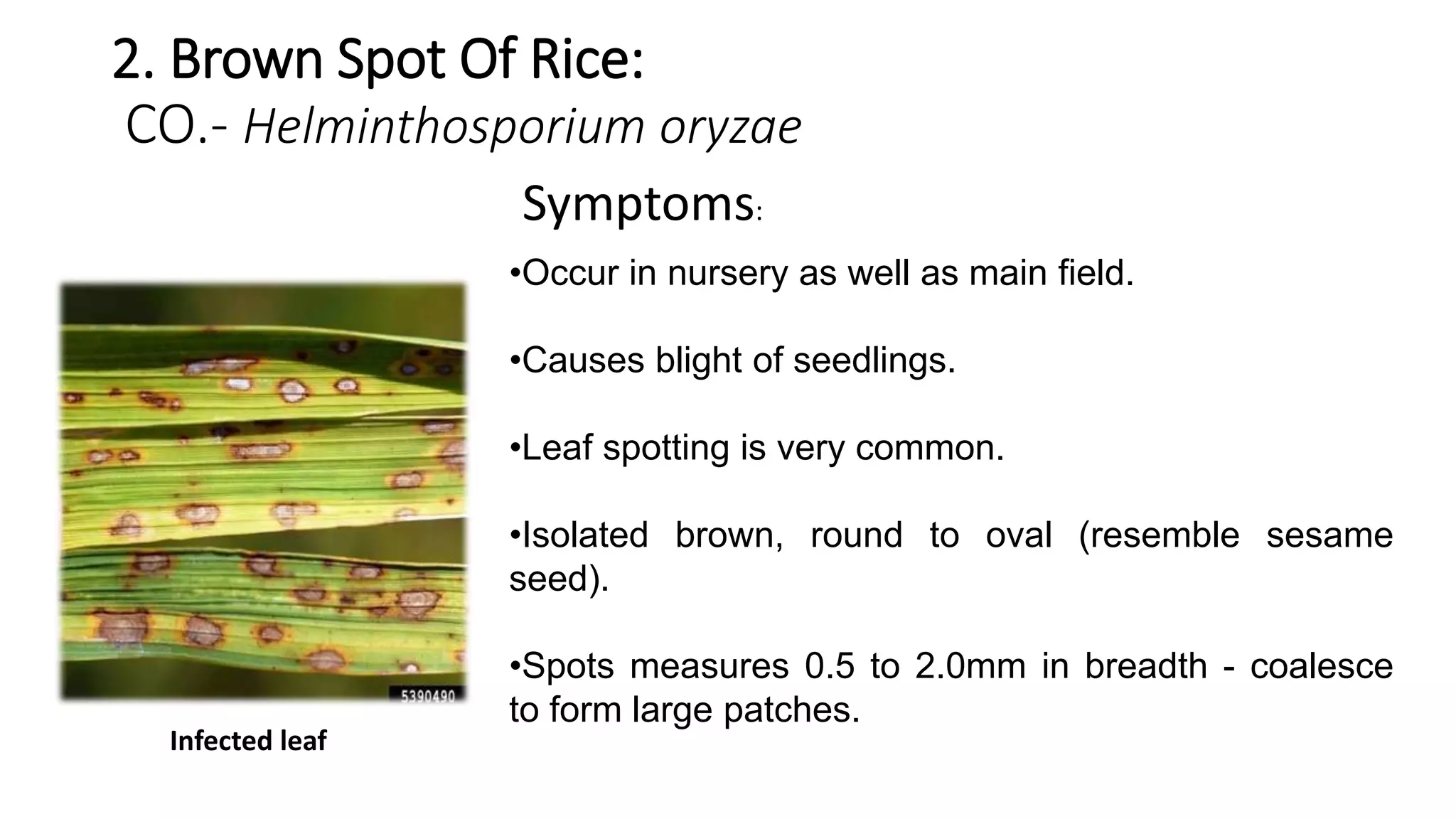
The document provides a detailed overview of major rice crop diseases, including their causal organisms, symptoms, infection cycles, and management practices. Key diseases discussed include rice blast, brown spot, bacterial blight, sheath blight, false smut, khaira disease, and tungro disease, highlighting their etiology and prevention methods. Recommended management strategies encompass cultural practices, the use of resistant varieties, and chemical treatments tailored to each disease.
















![Xanthomonas oryzae
Life Cycle of Xanthomonas oryzae
Fig 1 . Disease cycle of bacterial blight of rice caused by
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Reprinted from [ 67 ]
with permission from APS Press.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diseasesofrice-190723134255/75/Diseases-of-rice-19-2048.jpg)